User Guide
Introduction

GoMedic is a cross-platform desktop application written in Java and designed for doctors and medical residents to manage contacts and patient details. We aim for GoMedic to be used by someone who can type fast and take advantage of the optimized features for Command Line Interface.
GoMedic is bootstrapped using SE-EDU Address Book 3 and inherits some of its features such as clear, parameter
formatting, etc.
![]() Best Way To Read This User Guide:
Best Way To Read This User Guide:
It is best to open this User Guide using e-pdf reader as it allows you to click the header of each section that would
conveniently bring you to the table of content!
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Table of Contents
- 1. How To Use This Guide
- 2. Quick start
-
3. GoMedic Features
-
3.1 Patients Related Features
- 3.1.1 Overview
- 3.1.2 Adding a new patient:
add t/patient - 3.1.3 Deleting an existing patient:
delete t/patient - 3.1.4 List all patients:
list t/patient - 3.1.5 Updating an existing patient’s details:
edit t/patient - 3.1.6 Display full details of a patient:
view t/patient - 3.1.7 Clear all patient entries:
clear t/patient
- 3.2 Doctors Related Features
-
3.3 Activities Related Features
- 3.3.1 Overview
- 3.3.2 Adding a new activity:
add t/activity - 3.3.3 Adding a new appointment:
add t/appointment - 3.3.4 Deleting an existing activity:
delete t/activity - 3.3.5 List all activities:
list t/activity - 3.3.6 Updating an existing activity’s details:
edit t/activity - 3.3.7 Clear all activity and appointment entries:
clear t/activity
- 3.4. Finding entries
- 3.5. General Utility Commands
-
3.1 Patients Related Features
- 4. Tips and Tricks
- 5. FAQ
- 6. Command summary
1. How To Use This Guide
This user guide provides information to assist you in using GoMedic based on the features that you are most interested in. The user guide is sectioned such that each chapter has an
- Overview : Explains what the feature does and provides some important reminders about the notations used in that particular chapter
-
Features : List of commands available within that section
- Format : List of fields that need to be supplied for that particular command
- Parameters : Explanation about each field, together with its constraints
- Examples : Tutorial with pictures on how to use the commands.
To get the most out of this user guide, it would be best to understand the terminologies and notations that would often be used in this user guide.
Don’t worry if you forget some notations along the way, you can always check this chapter or the Overview section to find the important notations that are used in that chapter.
1.1 How GoMedic Looks Like
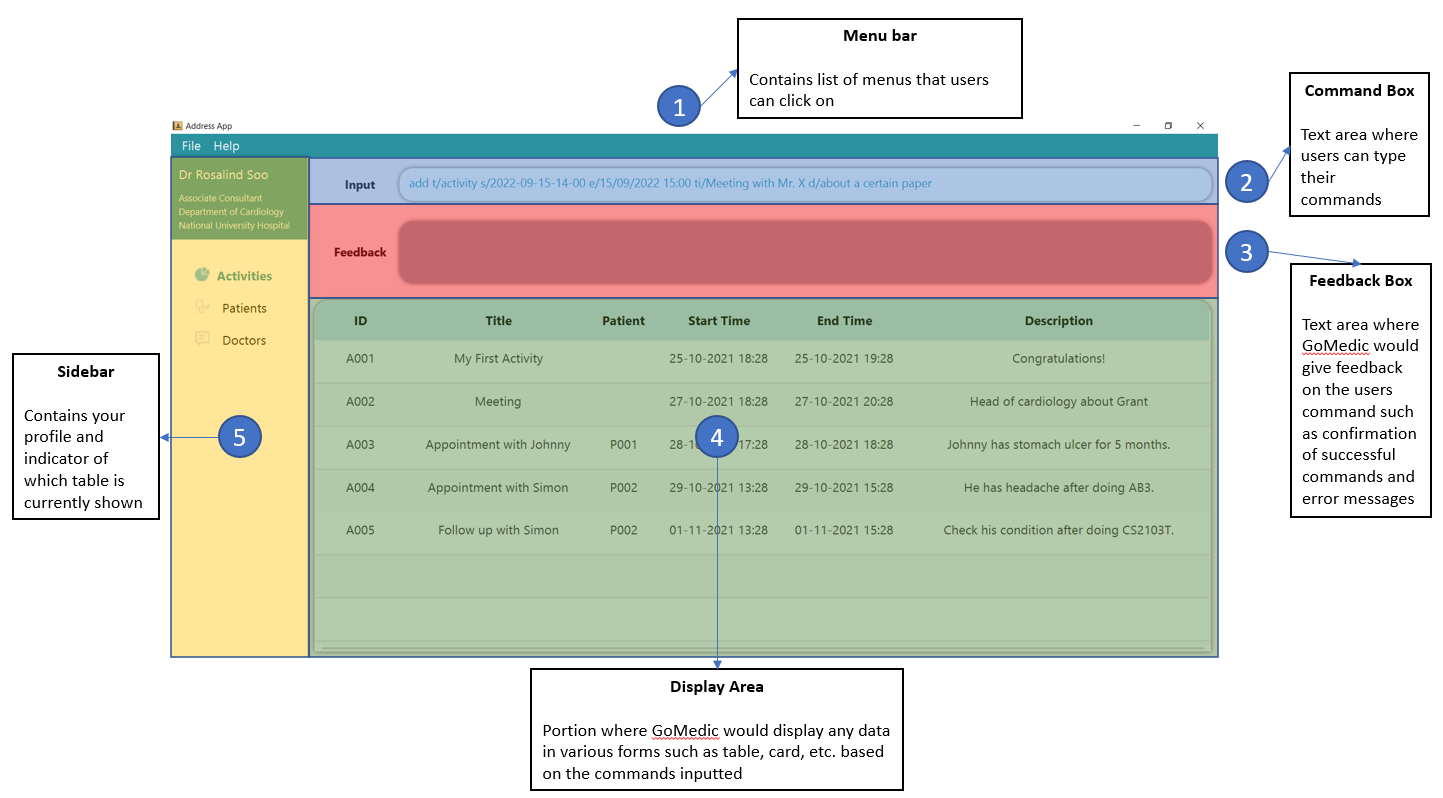
1.2 About the Commands
![]() Understanding The Notations:
Understanding The Notations:
-
Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters to be supplied by the user.
e.g. inadd n/NAME,NAMEis a parameter which can be used asadd n/John Doe. -
Items in square brackets are optional.
e.g.n/NAME [t/TAG]can be used asn/John Doe t/friendor asn/John Doe. -
Items with
… after them can be used multiple times including zero times.
e.g.[m/MEDICAL_CONDITION]…can be used asm/diabetes,m/fever m/fluetc. -
Parameters can be in any order.
e.g. if the command specifiesn/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER,p/PHONE_NUMBER n/NAMEis also acceptable. -
If a parameter is expected only once in the command but you specified it multiple times, only the last occurrence of the parameter will be taken.
e.g. if you specifyp/12341234 p/56785678, onlyp/56785678will be taken. -
Extraneous parameters for commands that do not take in parameters (such as
helpandexit) will be ignored.
e.g. if the command specifieshelp 123orhelp x/123, it will be interpreted ashelp. -
Any whitespaces inserted before and after the parameter value will be removed.
E.g. Let\srepresent a whitespace. If parameter is specified asp/\s\s98765432\s\s, the value will be treated as98765432, without the leading and trailing whitespaces.
1.3. Error Messages
-
Should you enter an invalid command that GoMedic cannot recognize, GoMedic will return some suggestions on the closest commands that you can choose from!
- For example, as
listcommand is not available, GoMedic will return you the closest commands available which arelist t/acitivty,list t/patient, andlist t/doctor.
To understand more how the suggestion works, please refer to this section.
- For example, as
-
Should you enter a valid command that GoMedic recognizes, but in an invalid format (such as a command with missing parameters), GoMedic would highlight the command in red and show the correct command usage in the feedback box.
-
Should you enter a valid command in a valid format, but with invalid parameters, GoMedic would flag the invalid parameter in the feedback box.
- Invalid parameters can be caused by constraints’ violation. For e.g., inputting
Xfor a patient’sBLOOD_TYPEfield will cause a violation to occur becauseXis not a valid blood type. - If multiple parameters are invalid, GoMedic only flags the first invalid parameter, so that the user is not overwhelmed by the error messages!
- Invalid parameters can be caused by constraints’ violation. For e.g., inputting
2. Quick start
-
Ensure you have Java
11or above installed in your Computer. -
Download the latest
gomedic.jarfrom here. -
Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for your GoMedic.
- Double-click the file to start the app. If it’s not possible, open the terminal and set the current directory to the directory that
gomedic.jarresides in. Enter the commandjava -jar gomedic.jar. If you still find difficulties in opening thegomedic.jarfile, please follow the steps here! - A GUI, similar to the one shown below, should appear in a few seconds. Note how the app
contains some sample data.
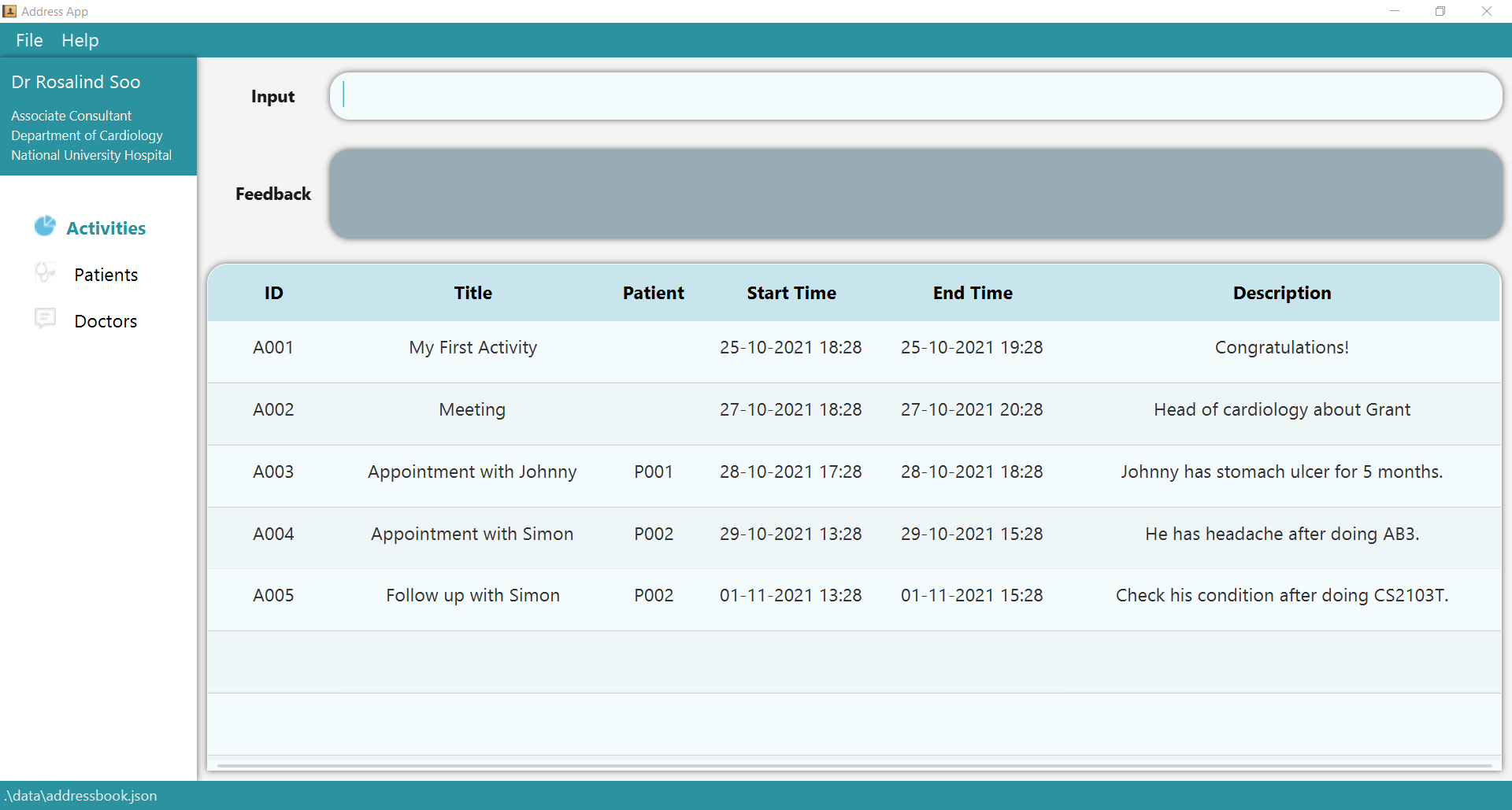
- Double-click the file to start the app. If it’s not possible, open the terminal and set the current directory to the directory that
-
Type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it. E.g. typing
helpand pressing Enter will open the help window.
Some example commands you can try:-
list t/patient: Lists all patients. -
add t/patient n/John Doe a/30 g/M h/174 w/72 b/O p/12345678 m/heart-failure m/diabetes: Adds a patient namedJohn Doeto GoMedic. -
delete t/patient P001: Deletes the patient whose id is P001. -
clear: Deletes all contacts including patients, doctors, and activities. -
exit: Exits the app.
-
-
Address Book, GoMedic Address Book, and GoMedic refers to the same term, which is the application itself.
3. GoMedic Features
3.1 Patients Related Features
3.1.1 Overview
Patients related features allow you to store, edit, view, and list patients.
Using these patient related features, you can store your patients’ details and track all medical conditions that your patients are diagnosed with.
Each patient is uniquely identified by his / her PATIENT_ID in the form of PXXX, where XXX is a 3-digit integer.
Therefore, two patients with exactly same NAME, PHONE_NUMBER, AGE, GENDER, HEIGHT, WEIGHT, BLOOD_TYPE,
and MEDICAL_CONDITIONS with different PATIENT_ID are considered distinct.
![]() Reminder on Command Notation:
Reminder on Command Notation:
- Some important notation in reading the commands
-
[flag/KEYWORD]indicates optional parameters -
flag/KEYWORDindicates mandatory parameters
-
3.1.2 Adding a new patient: add t/patient
Adds a new patient into your GoMedic application.
Format: add t/patient n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER a/AGE g/GENDER h/HEIGHT w/WEIGHT b/BLOOD_TYPE [m/MEDICAL_CONDITION]...
GoMedic would create a new patient based on the smallest PATIENT_ID available.
- GoMedic would check for any invalid parameters as specified here. Should there be any, the new patient will not be added.
The parameters are :
| Parameters | Explanation | Constraints |
|---|---|---|
n/NAME |
full name of the patient | must only contain alphanumeric characters and spaces, and it should not be blank |
p/PHONE_NUMBER |
phone number of the patient | must be entirely numeric and exactly 8 digits long |
g/GENDER |
gender of the patient | must be M/F/O where M is for Male, F is for Female, and O is for Others, all non capitalized letters will be capitalized, e.g. m input will be treated as M
|
h/HEIGHT |
height of the patient in centimeters | must be integer between 1 and 300 inclusive |
w/WEIGHT |
weight of the patient in kilograms | must be integer between 1 and 700 inclusive |
b/BLOOD_TYPE |
blood type of the patient | must be A+/A-/B+/B-/AB+/AB-/O+/O-, all non capitalized letters will be capitalized, e.g. a+ input will be treated as A+
|
m/MEDICAL_CONDITION |
list of patient’s past/pre-existing medical conditions | must only contain alphanumeric characters and spaces, with maximum of 30 characters |
![]() Extra Constraints
Extra Constraints
-
MEDICAL_CONDITIONis unique. - Duplicates of the same
MEDICAL_CONDITIONprovided will be discarded.
Example:
1. Type the command add t/patient n/John Smith p/98765432 a/45 b/AB+ g/M h/175 w/70 m/heart failure m/diabetes into
the command box.
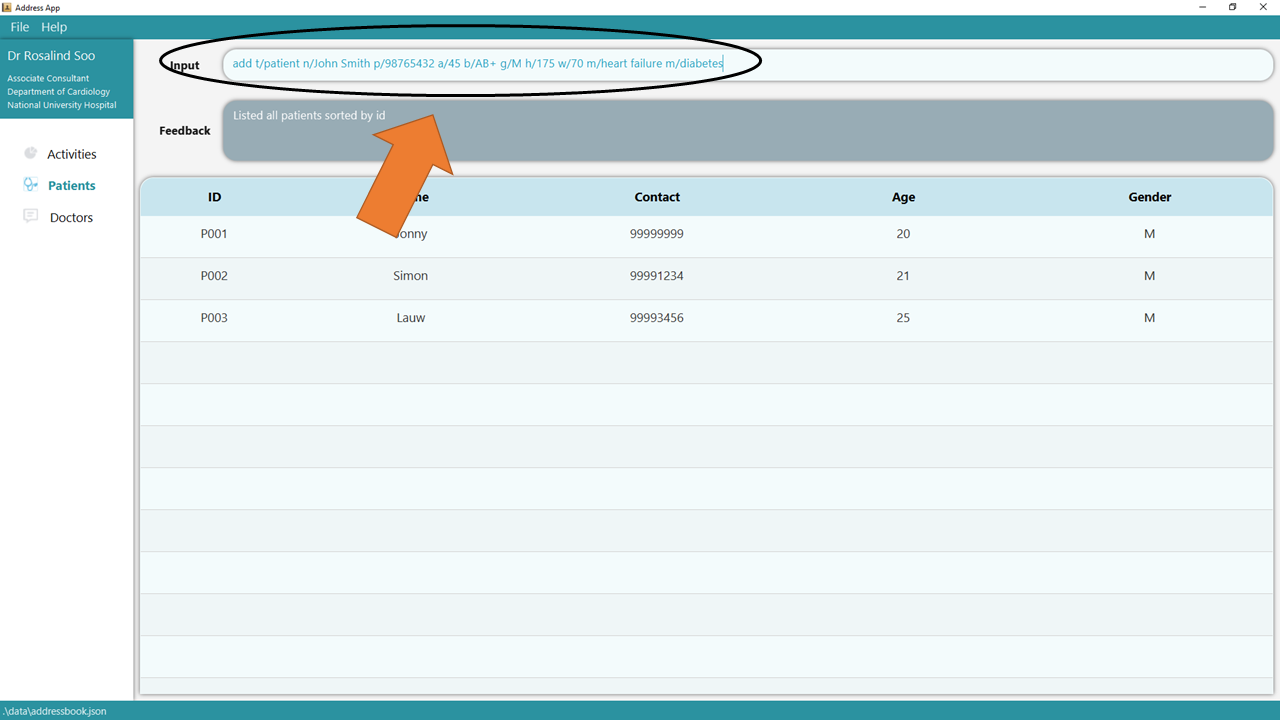
2. Press Enter and you should see the new entry being made in the Patient table! By default, the table would be sorted by ID.
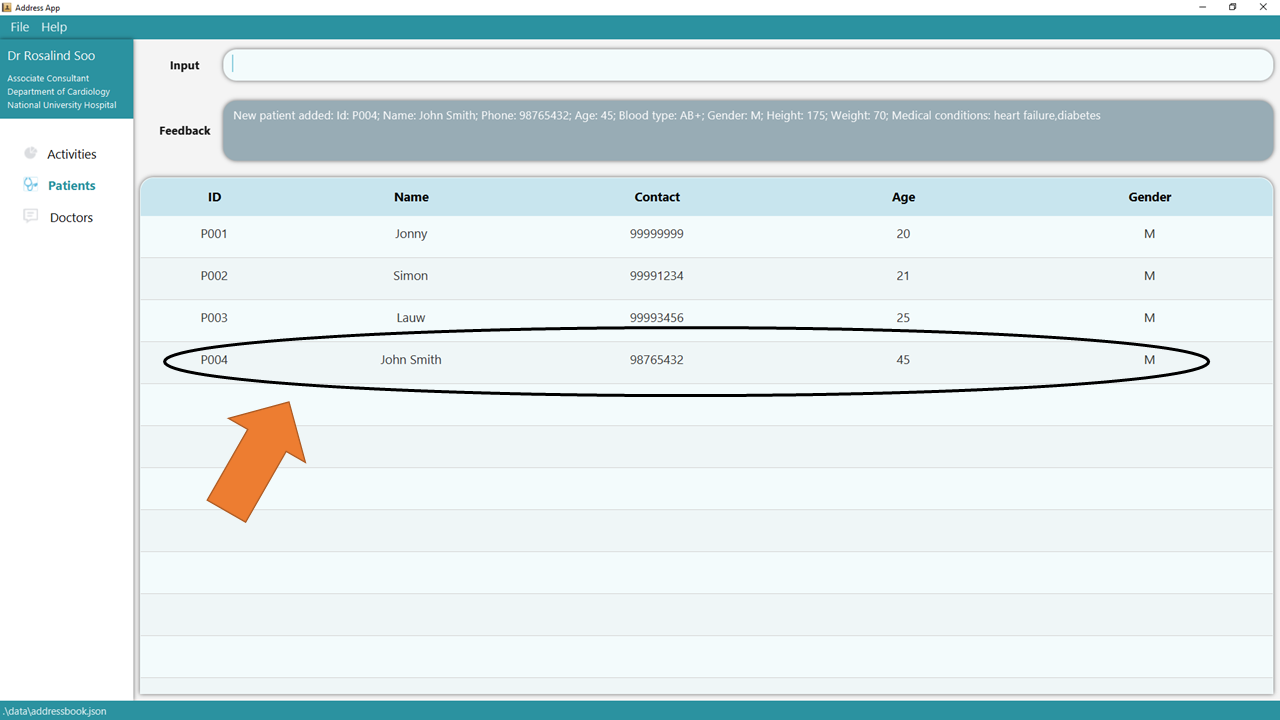
3. If there are any errors, the command would turn red as indicated by 1 and the feedback would be given in the feedback box at 2. In this case, the error is caused by the invalid gender input in the command. Fix the issue and press enter again! Now the command should work correctly!
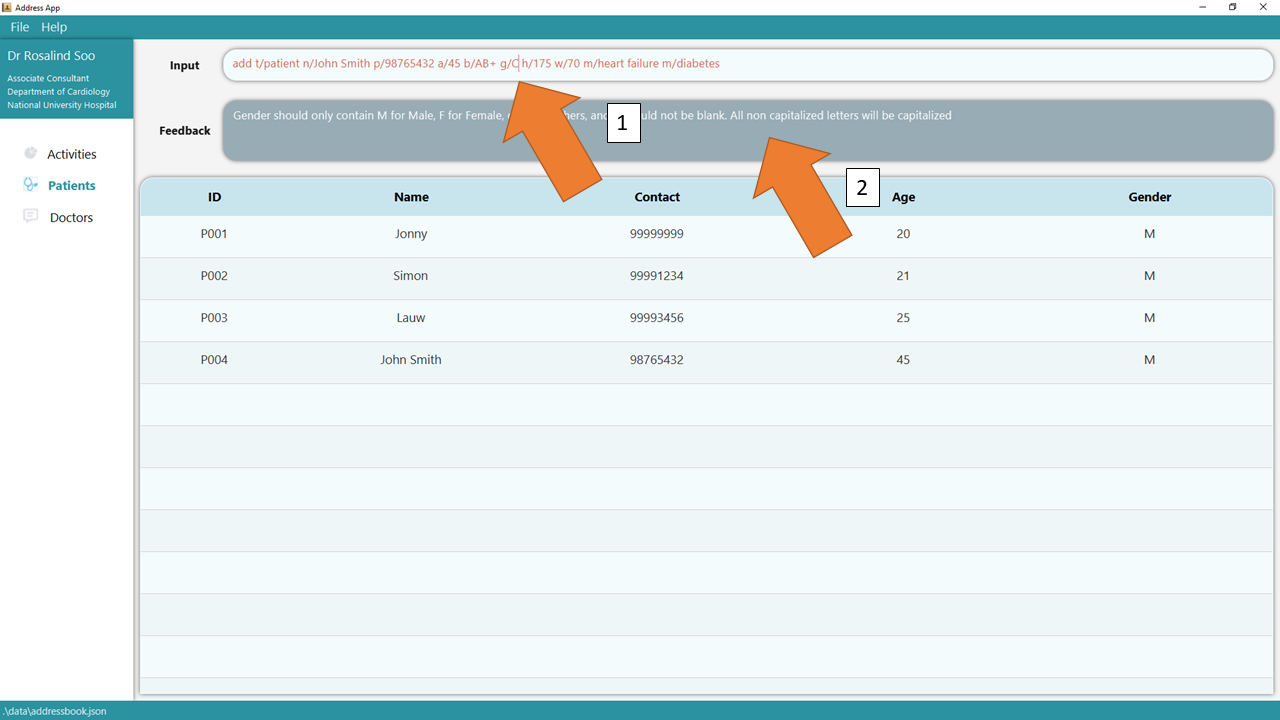
To understand better how GoMedic classifies the error messages, please refer to this section.
3.1.3 Deleting an existing patient: delete t/patient
Deletes an existing patient from GoMedic.
Format: delete t/patient PATIENT_ID
The parameter is:
| Parameters | Explanation | Constraints |
|---|---|---|
PATIENT_ID |
the Patient Id as shown by the Patient table (case-insensitive) | Must be in the form of PXXX / pXXX where XXX is 3-digit integer. For the full information, please refer to this
|
PATIENT_ID can be obtained by listing all the patients using list t/patient command
or searching for specific patients using find t/patient command.
Example:
1. Type the command delete t/patient P001 into the command box.
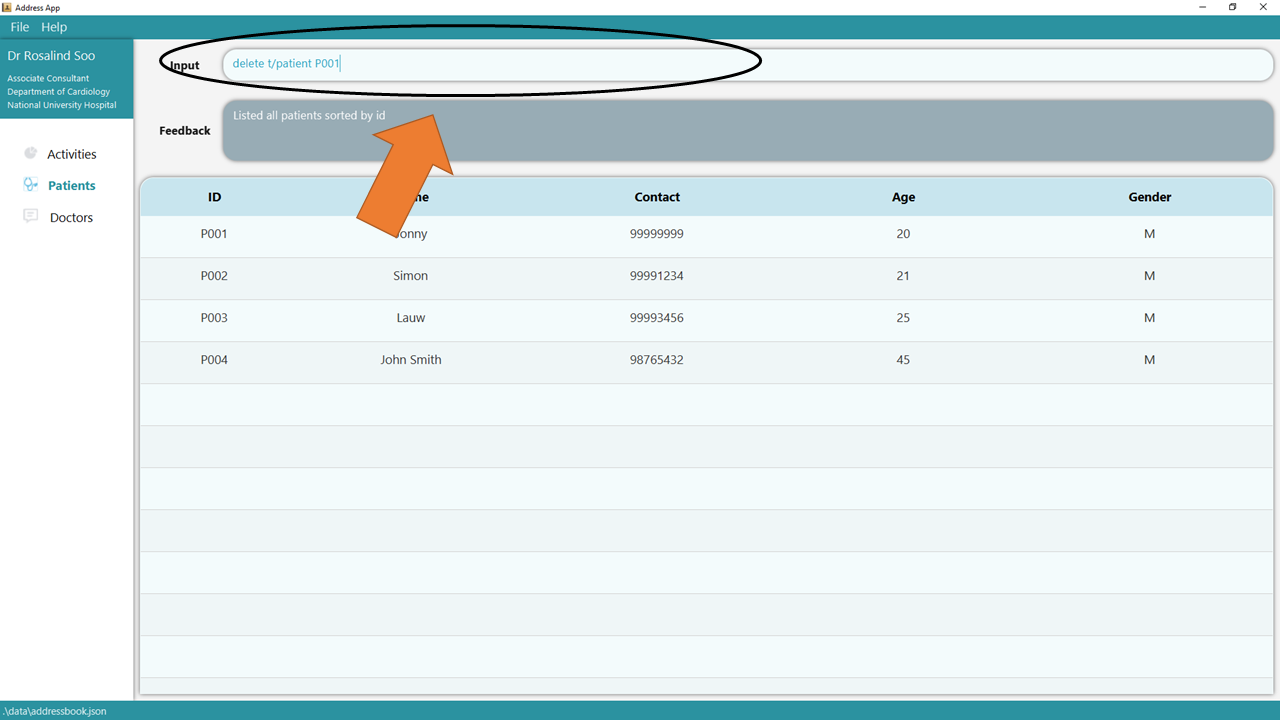
2. Press Enter and you will get confirmation that the patient is indeed deleted. Check that the patient, identified by his/her deleted ID, should not be there.
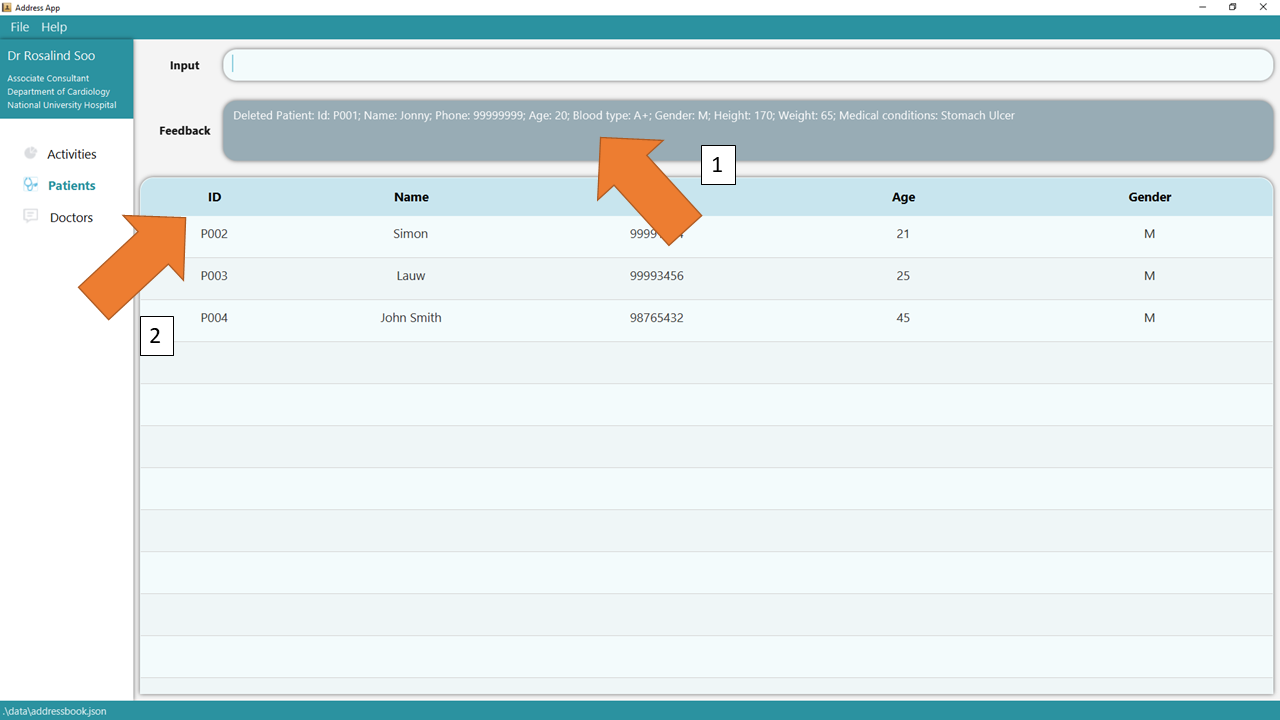
3. If there are any errors, the command would turn red as shown by 1. Also, feedback about the error is shown in the feedback box shown at 2. Fix the issue and the command should work correctly now!
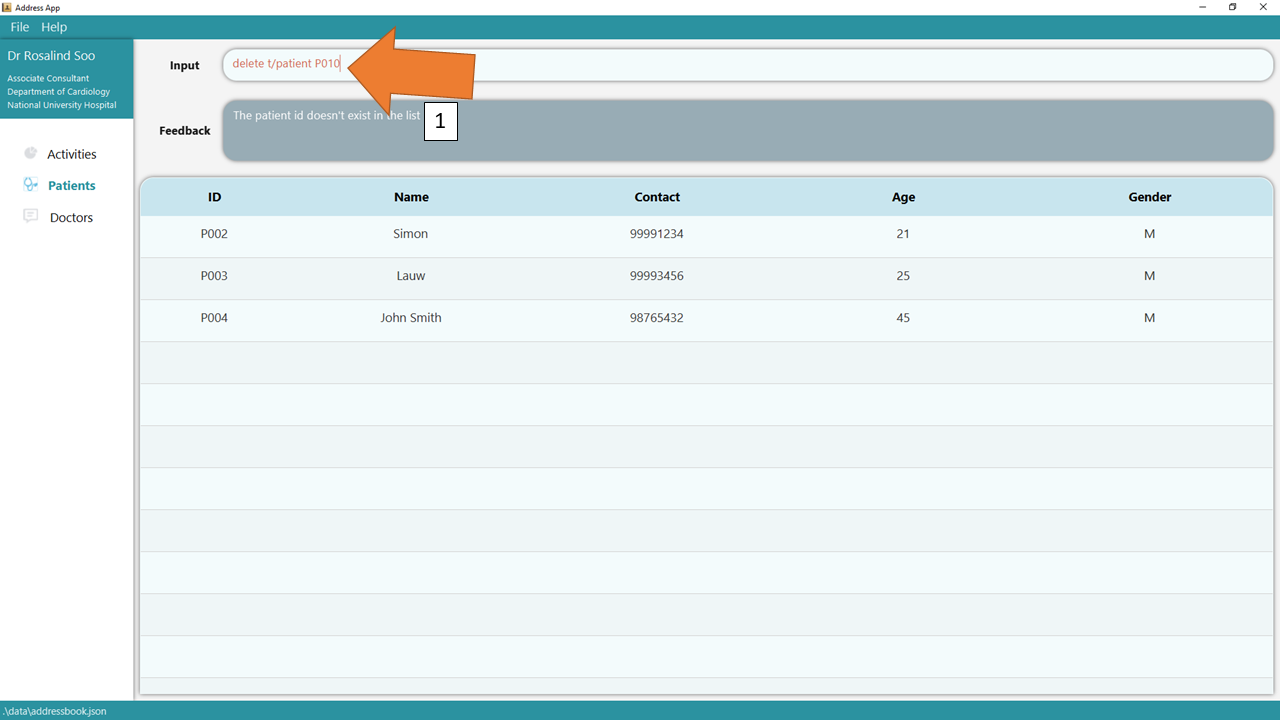
To understand better how GoMedic classifies the error messages, please refer to this section.
3.1.4 List all patients: list t/patient
List all patients that are stored in GoMedic.
Format: list t/patient
Example:
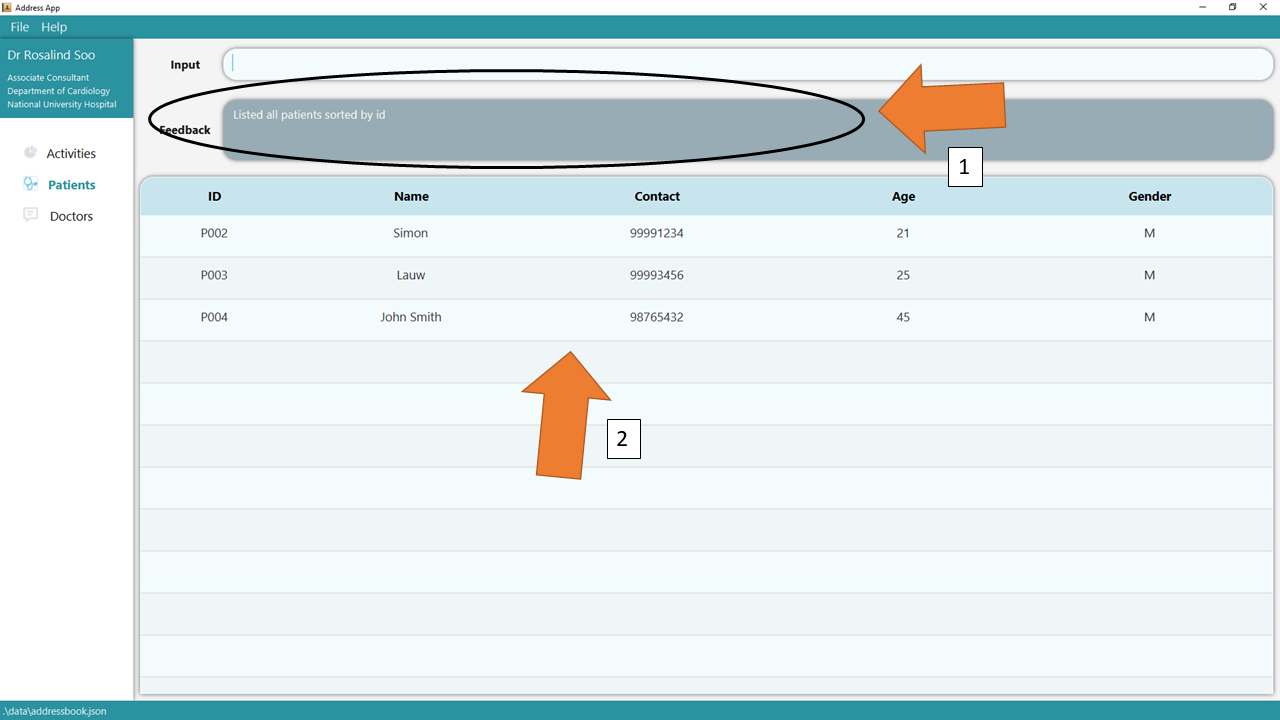
1. Type the command list t/patient into the command box and press Enter. The success confirmation should be shown by the feedback box as shown by 1.
GoMedic will display the Patient Table, as seen by 2.
3.1.5 Updating an existing patient’s details: edit t/patient
Edits a patient’s details in GoMedic.
Format: edit t/patient i/PATIENT_ID [OPTIONAL_PARAMETERS]...
![]() Caution:
Caution:
-
The
PATIENT_IDis assigned by GoMedic and cannot be modified at all once created. -
The
MEDICAL_CONDITIONSwill be replaced by the newMEDICAL_CONDITIONSsupplied in the edit command.
The parameters are:
| Parameters | Explanation | Constraints |
|---|---|---|
i/PATIENT_ID |
the unique identifier of a patient (case-insensitive) | must be in the form of PXXX / pXXX where XXX is 3-digit integer. For the full information, please refer to this
|
n/NAME |
full name of the patient | must only contain alphanumeric characters and spaces, and it should not be blank |
a/AGE |
age of the patient | must be integer between 0 and 150 inclusive |
p/PHONE_NUMBER |
phone number of the patient | must be entirely numeric and exactly 8 digits long |
g/GENDER |
gender of the patient | must be M/F/O where M is for Male, F is for Female, and O is for Others, all non capitalized letters will be capitalized, e.g. m input will be treated as M
|
h/HEIGHT |
height of the patient in centimeters | must be integer between 1 and 300 inclusive |
w/WEIGHT |
weight of the patient in kilograms | must be integer between 1 and 700 inclusive |
b/BLOOD_TYPE |
blood type of the patient | must be A+/A-/B+/B-/AB+/AB-/O+/O-, all non capitalized letters will be capitalized, e.g. a+ input will be treated as A+
|
m/MEDICAL_CONDITION |
list of patient’s past/pre-existing medical conditions | must only contain alphanumeric characters and spaces, with maximum of 30 characters |
Example:
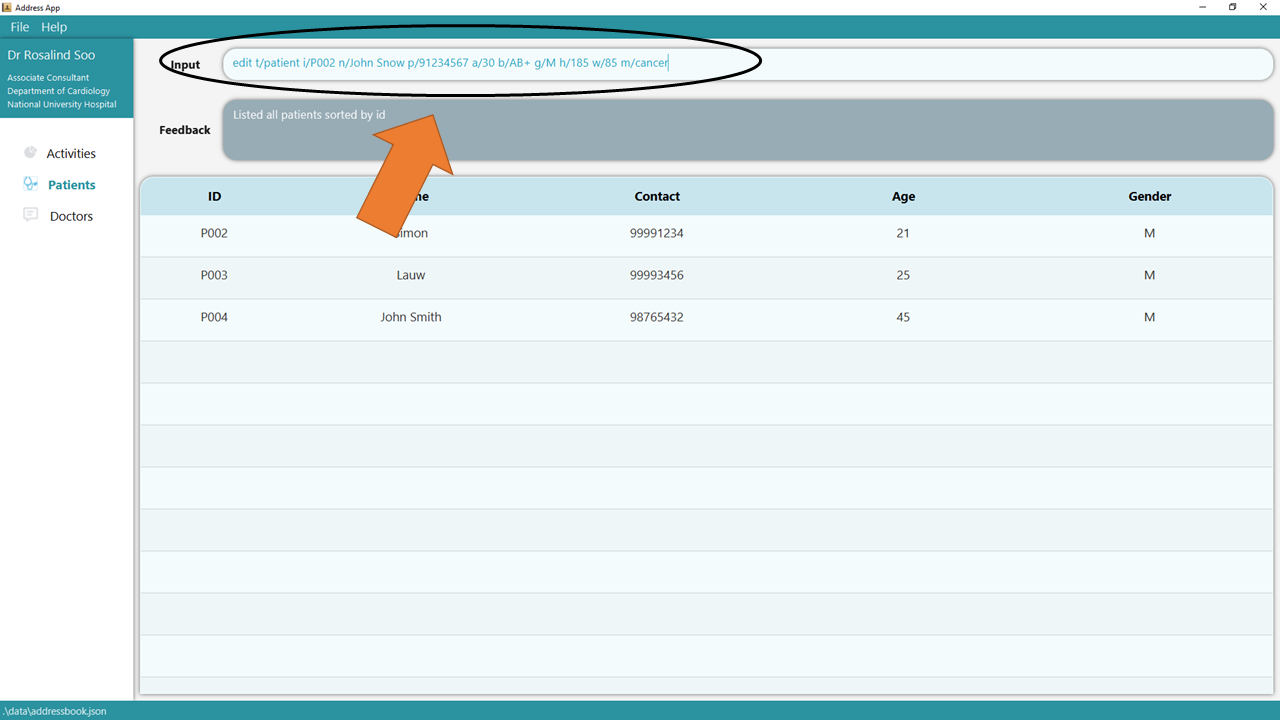
1. Type the command edit t/patient i/P002 n/John Snow p/91234567 a/30 b/AB+ g/M h/185 w/85 m/cancer into the command box.
Ensure that the edited patient, as identified by his/her PATIENT_ID, exists!
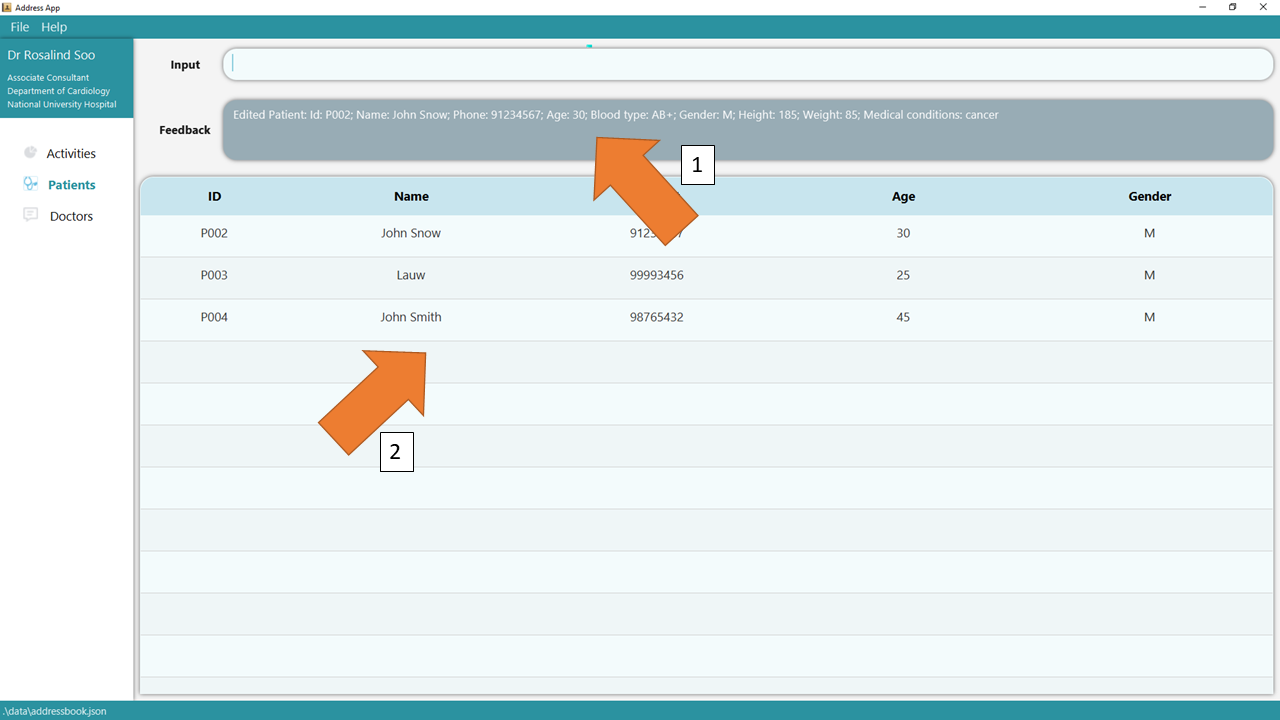
2. Press Enter and the success confirmation should be displayed in the feedback box as seen in 1. As shown by 2, patient P002 has his information updated!
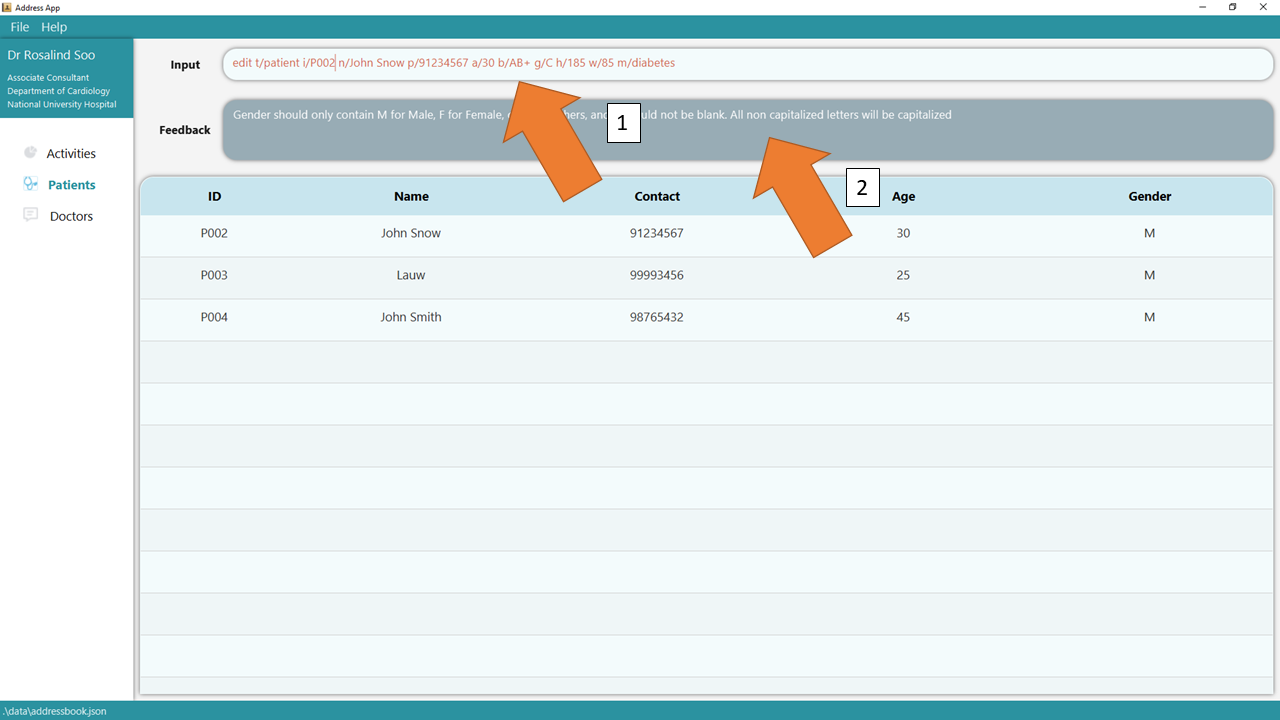
3. If there are any errors, the command would turn red as shown by 1. Also, feedback about the error will be displayed in the feedback box, as seen by 2.
In this case, the error is caused by an invalid gender supplied to the GENDER parameter. Fix the issue and the command should work correctly now!
To understand better how GoMedic classifies the error messages, please refer to this section.
3.1.6 Display full details of a patient: view t/patient
Displays the full details of a particular patient.
Format: view t/patient PATIENT_ID
The parameter is:
| Parameters | Explanation | Constraints |
|---|---|---|
PATIENT_ID |
the Patient Id as shown by the Patient table (case-insensitive) | Must be in the form of PXXX / pXXX where XXX is 3-digit integer. For the full information, please refer to this
|
PATIENT_ID can be obtained by listing all the patients using list t/patient command
or searching for the specific patient using find t/patient command.
Example:
1. Type the command view t/patient into the command box.
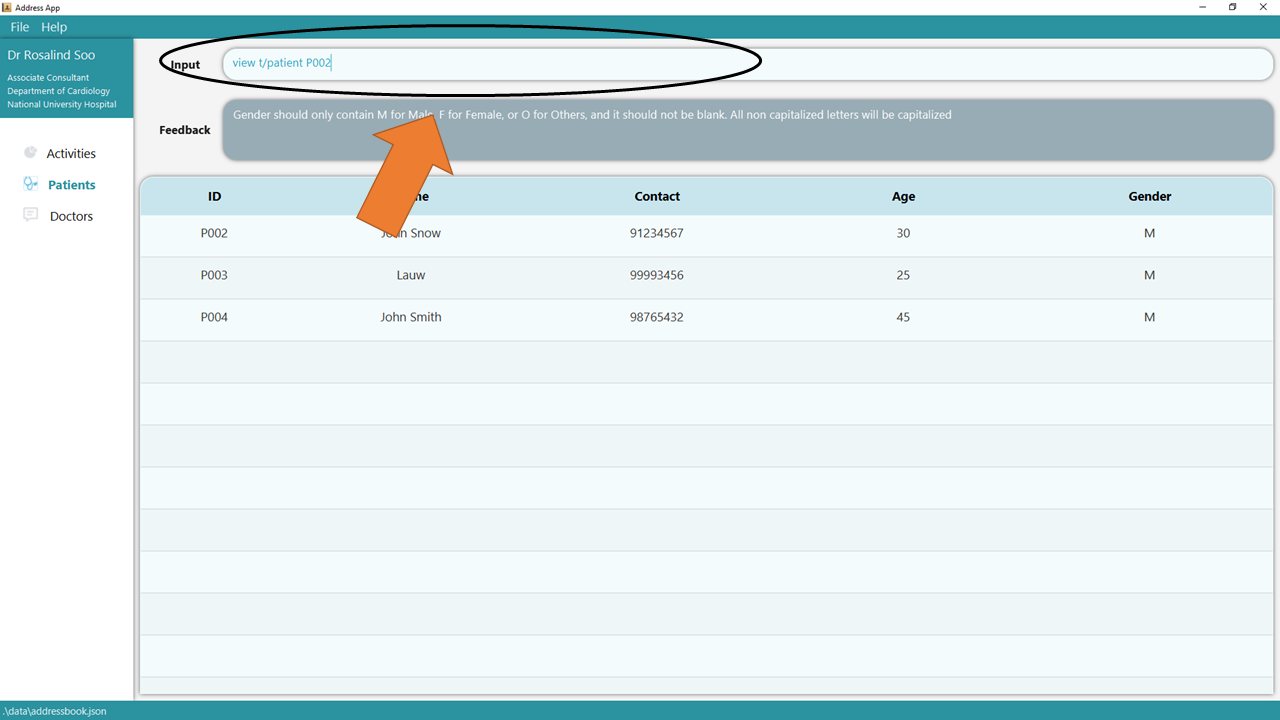
2. Press Enter and the details of the patient will be shown in the screen.
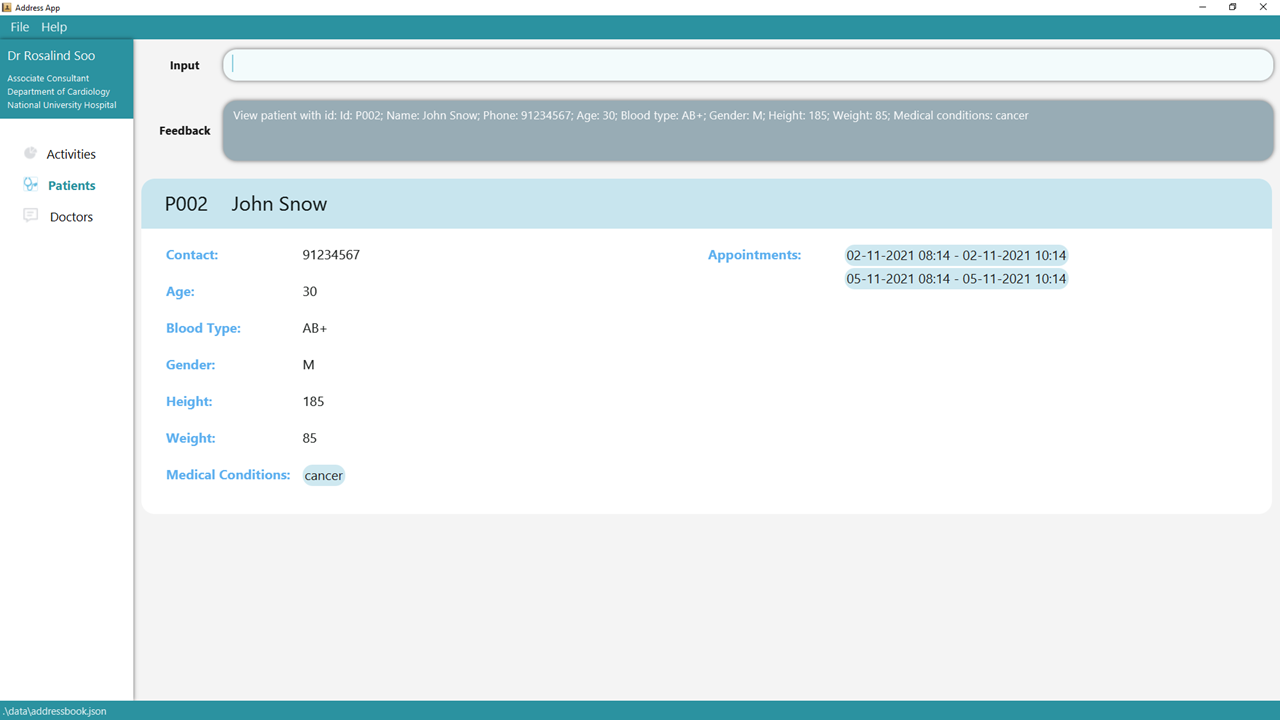
3.1.7 Clear all patient entries: clear t/patient
Clears all patient entries from GoMedic.
Format: clear t/patient
Example:
1. Type the command clear t/patient into the command box. Press Enter and all the patients will be deleted.
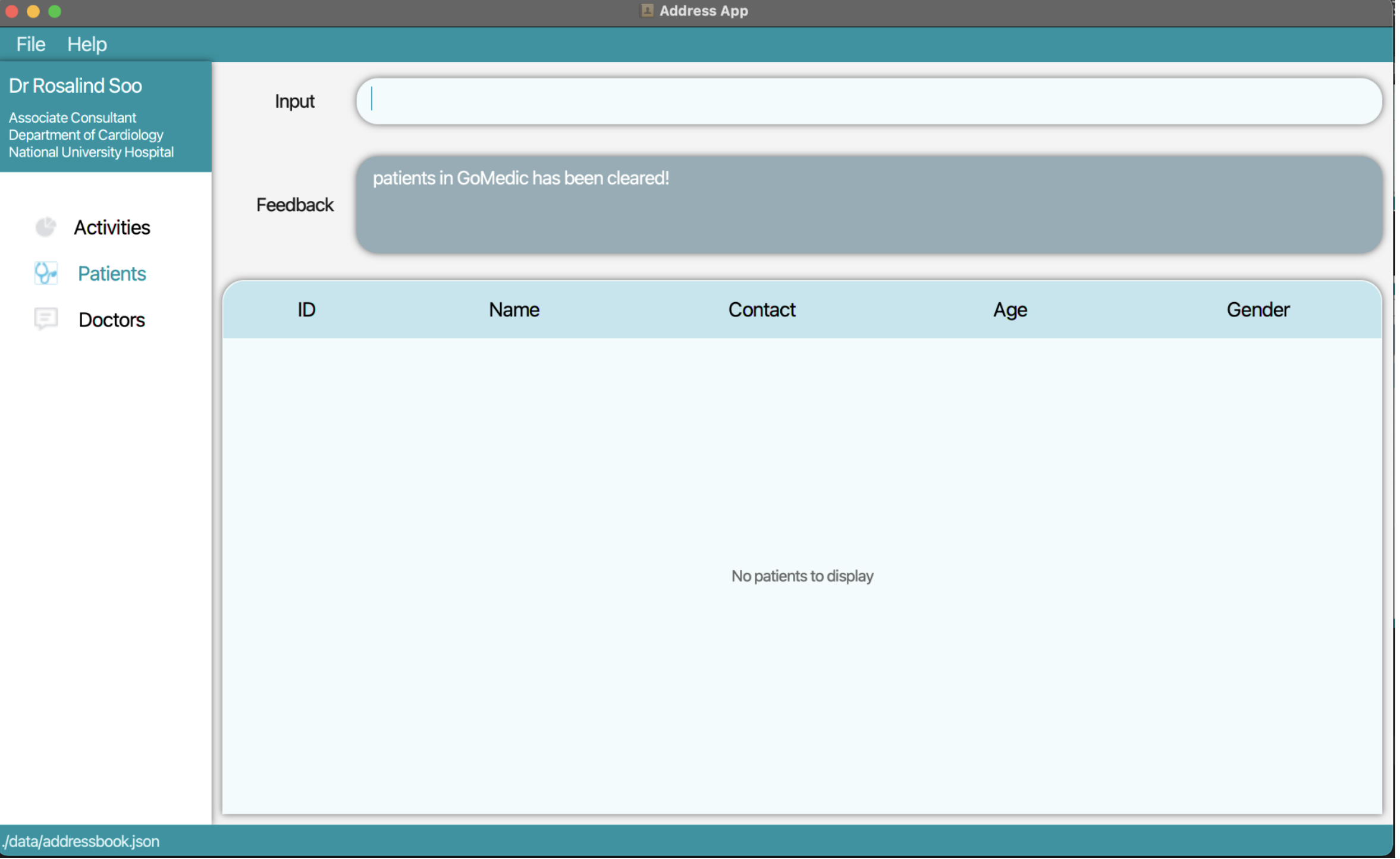
![]() Warning:
This will also delete all corresponding appointments since there are no more patients in GoMedic.
See more about appointments here
Warning:
This will also delete all corresponding appointments since there are no more patients in GoMedic.
See more about appointments here
3.2 Doctors Related Features
3.2.1 Overview
Doctor related features allow you to store, edit and list details of other doctors.
These could be details of your colleagues, or other acquaintances that are important in your work.
Each doctor is uniquely identified by his or her DOCTOR_ID in the form DXXX, where XXX is a 3-digit integer.
Therefore, GoMedic considers two doctors with the same details (same NAME, PHONE_NUMBER and DEPARTMENT),
as two distinct and different doctors, as long as their DOCTOR_IDs are different.
![]() Reminder on Command Notation:
Reminder on Command Notation:
- Some important notation in reading the commands
-
[flag/KEYWORD]indicates optional parameters -
flag/KEYWORDindicates mandatory parameters
-
3.2.2 Adding a new doctor’s details: add t/doctor
Adds the details of a doctor into GoMedic.
Format: add t/doctor n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER de/DEPARTMENT
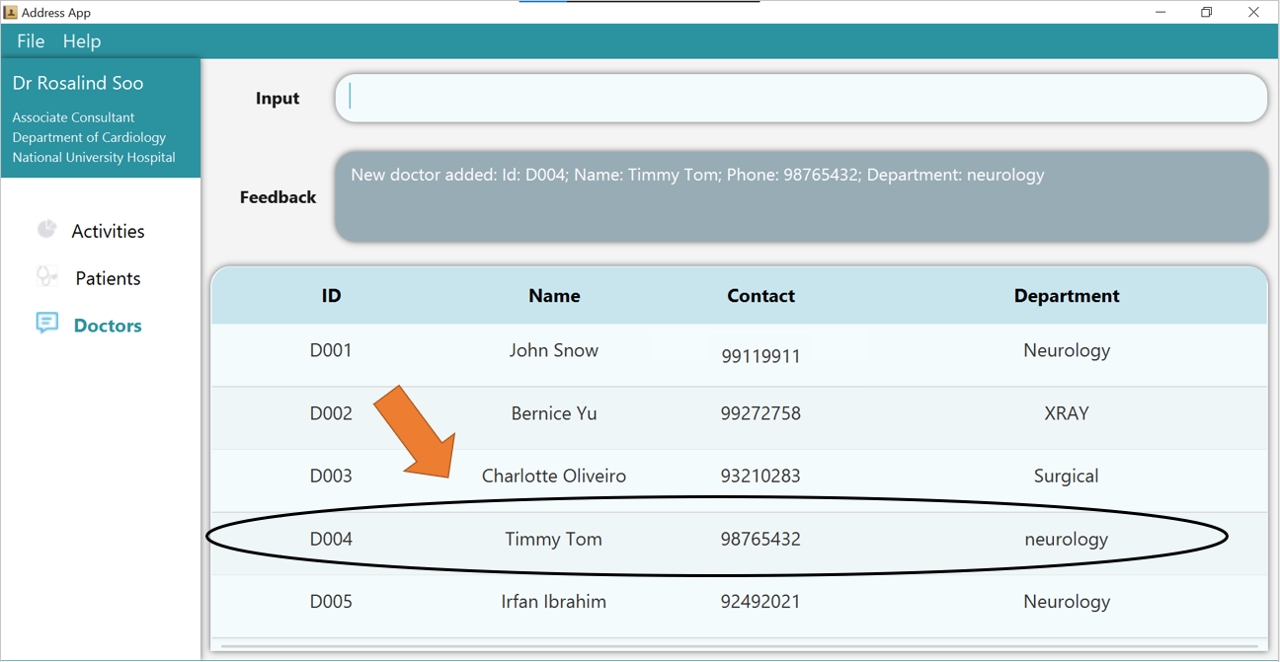
GoMedic creates a new doctor based on the smallest Doctor ID available. This example is shown here, where a new doctor is added and assigned the ID D004 instead of D006.
NOTE:
- A new added doctor may not be displayed as the last entry, as the table is sorted by ID.
- If there are any invalid parameters, as specified here, the new doctor will not be added.
The parameters are:
| Parameters | Explanation | Constraints |
|---|---|---|
n/NAME |
the name of the doctor. | must only contain alphanumeric characters and spaces, and it should not be blank |
p/PHONE_NUMBER |
the phone number of the doctor. | must be entirely numeric and exactly 8 digits long |
de/DEPARTMENT |
the department of the doctor. | must only contain alphanumeric characters and spaces, and it should not be blank |
1. Type the command add t/doctor n/Timmy Tom p/98765432 de/neurology into the command box.
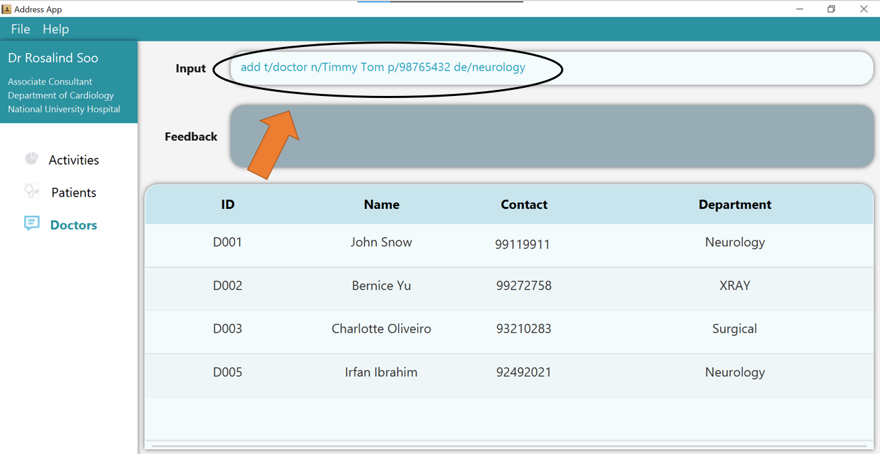
2. Press Enter and you should see the new entry being made in the Doctor table!
Note that the table is sorted by ID. Hence, in this example, the new entry will not be displayed as the last entry!
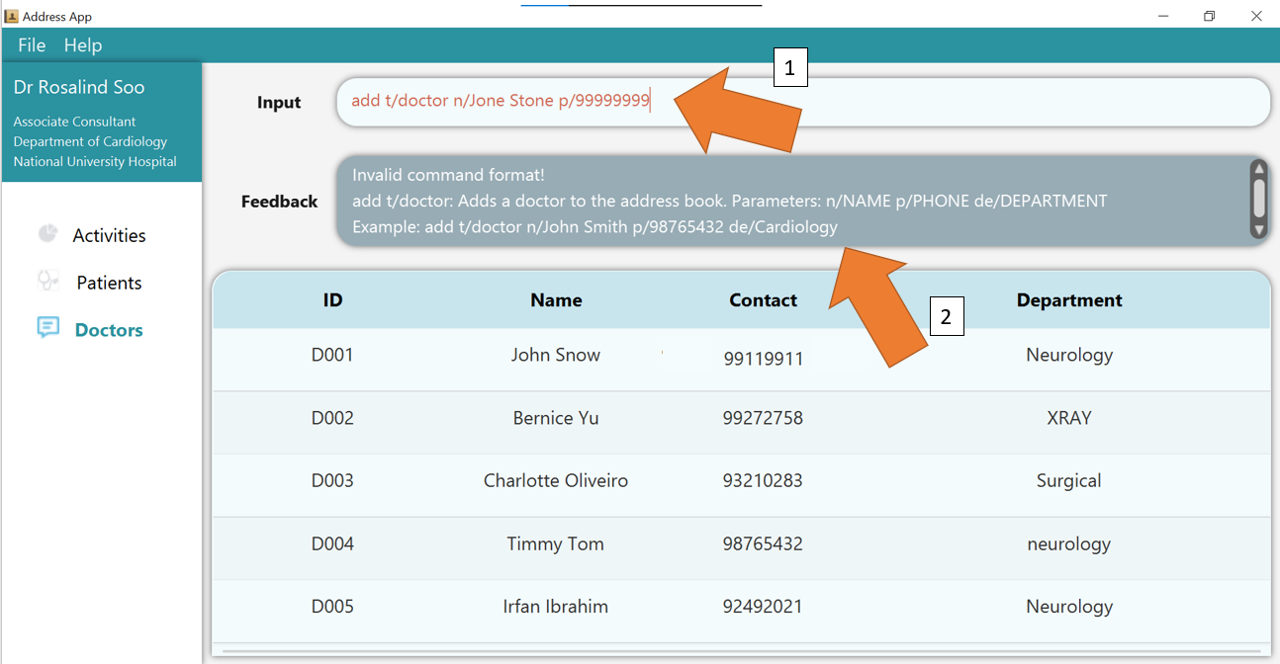
3. If there are any errors, the command would turn red as shown by 1.
In the example below, the user has forgotten to include the DEPARTMENT of the doctor.
Fix the issue by following the command format, shown in 2, and press Enter again; The command should work correctly now!
To understand better how GoMedic classifies the error messages, please refer to this section.
3.2.3 Deleting an existing doctor: delete t/doctor
Deletes an existing doctor from GoMedic.
Format: delete t/doctor DOCTOR_ID
DOCTOR_ID does not require additional flags such as i/! Supplying those flags would render the command invalid!
The parameter is:
| Parameter | Explanation | Constraint |
|---|---|---|
DOCTOR_ID |
the Doctor Id as shown by the Doctor table (case-insensitive) | Must be in the form of DXXX / dXXX where XXX is 3-digit integer. For the full information, please refer to this
|
DOCTOR_ID can be obtained by listing all the doctors using list t/doctor command
or searching for the specific doctor using find t/doctor command.Example:
1. Type the command delete t/doctor D001 into the command box.
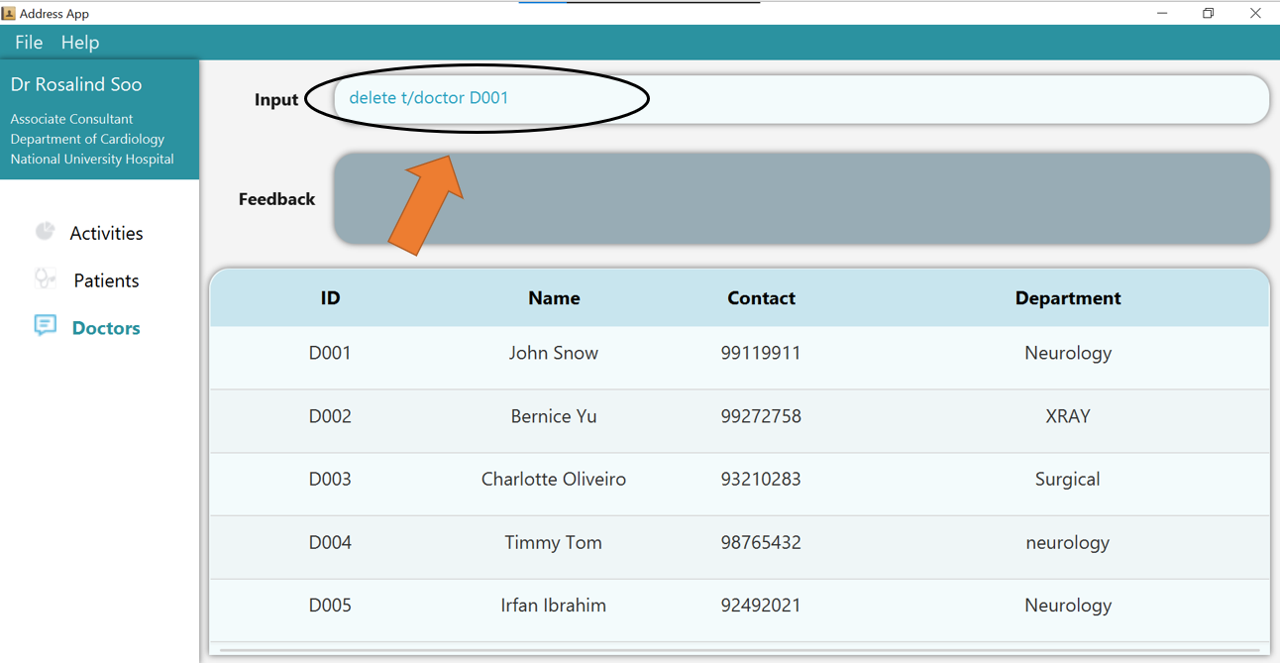
2. Press Enter and you will get confirmation that the doctor is indeed deleted.
Check the doctor table. The doctor, identified by his/her deleted ID, should not be there.
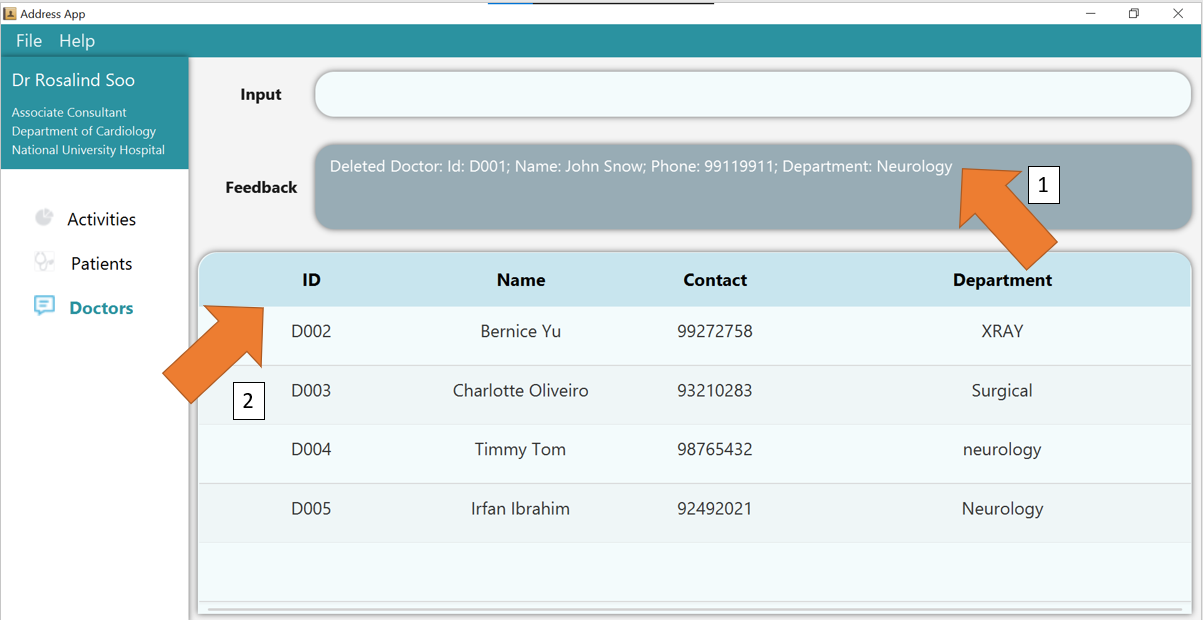
3. If there are any errors, the command would turn red as shown by 1. Also, feedback about the error is displayed in the feedback box, as seen by 2. Fix the issue and the command should work correctly now!
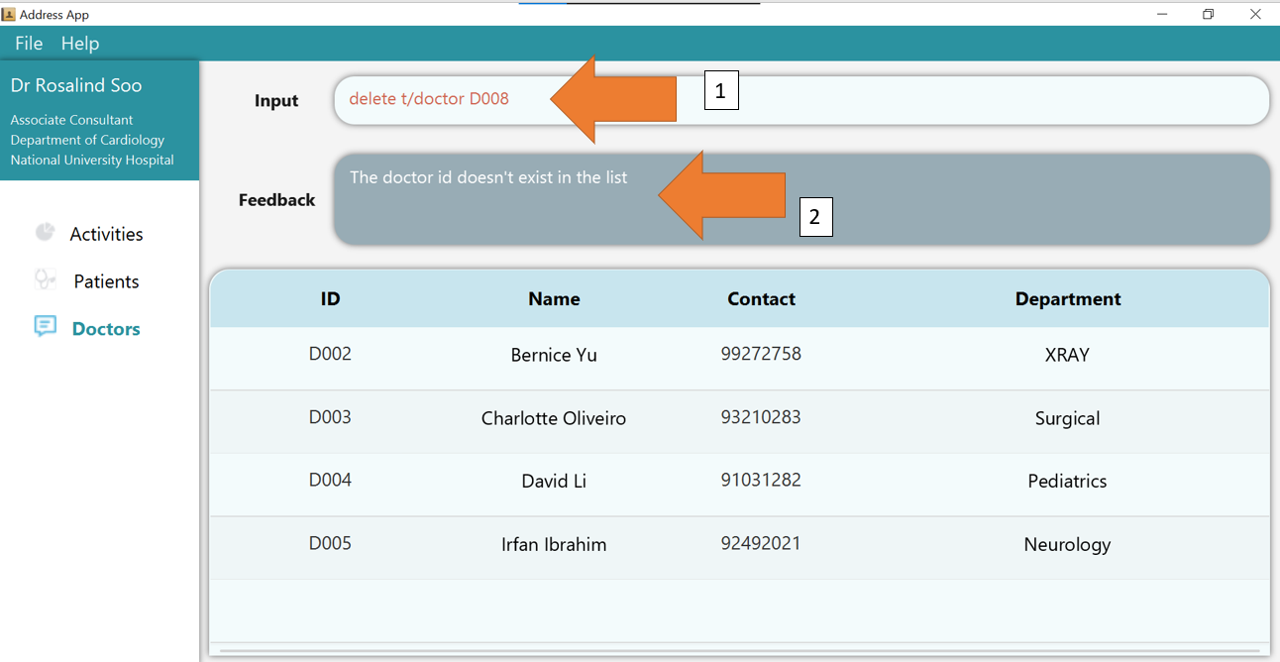
To understand better how GoMedic classifies the error messages, please refer to this section.
3.2.4 List all doctors: list t/doctor
List all doctors that are stored in GoMedic.
Format: list t/doctor
Example:
Type the command list t/doctor into the command box. Press Enter and the list of doctors will be displayed, as shown below.
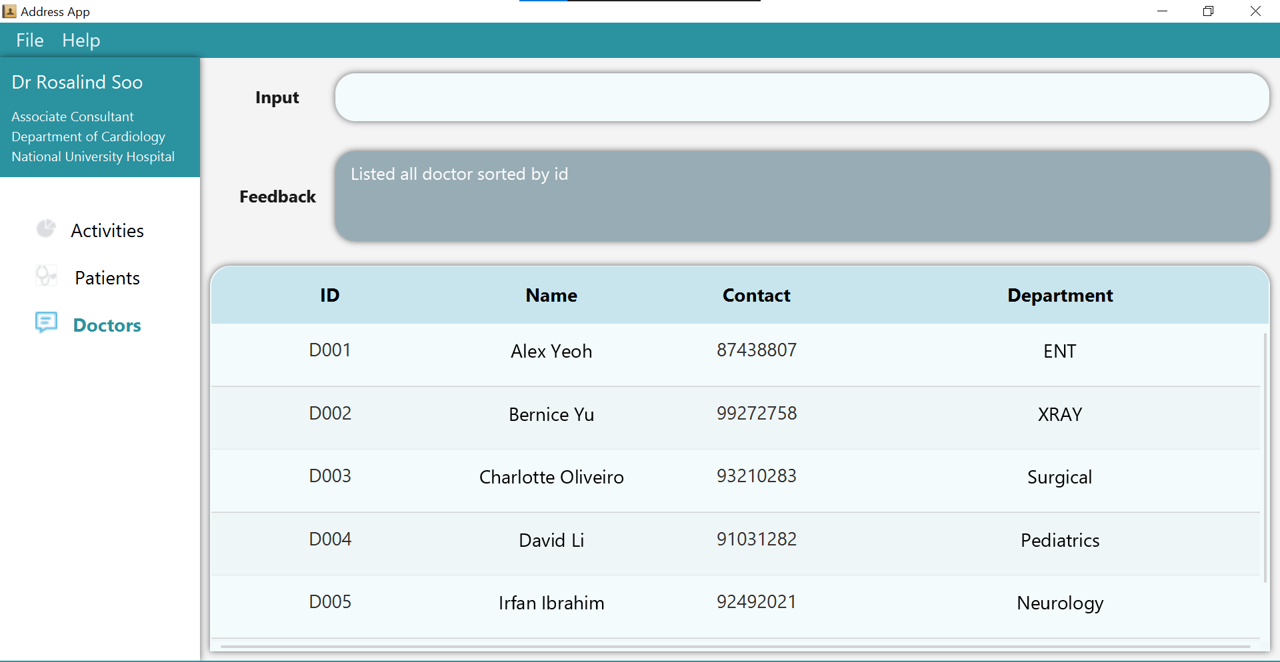
3.2.5 Updating an existing doctor’s details: edit t/doctor
Edits a doctor’s details in GoMedic.
Format: edit t/doctor i/DOCTOR_ID [OPTIONAL_PARAMETERS]...
When editing an existing doctor, all parameters are optional except DOCTOR_ID! However,
- If there are no parameters being supplied at all besides the
DOCTOR_ID, GoMedic would return an error. - The new information supplied to the
edit t/doctorcommand would still need to conform to the constraints as stated above.
![]() Caution:
Caution:
The DOCTOR_ID is assigned by GoMedic and cannot be modified at all once created.
The parameters are:
| Parameters | Explanation | Constraints |
|---|---|---|
i/DOCTOR_ID |
the unique identifier of a doctor (case-insensitive). | Must be in the form of DXXX / dXXX where XXX is 3-digit integer. For the full information, please refer to this
|
n/NAME |
the name of the doctor. | Must only contain alphanumeric characters and spaces, and it should not be blank |
p/PHONE_NUMBER |
the phone number of the doctor. | Must be entirely numeric and exactly 8 digits long |
de/DEPARTMENT |
the department of the doctor. | Must only contain alphanumeric characters and spaces, and it should not be blank |
Example:
1. Type the command edit t/doctor i/D002 de/Radiology into the command box. Ensure that the edited doctor, as identified by his or her DOCTOR_ID, exists!
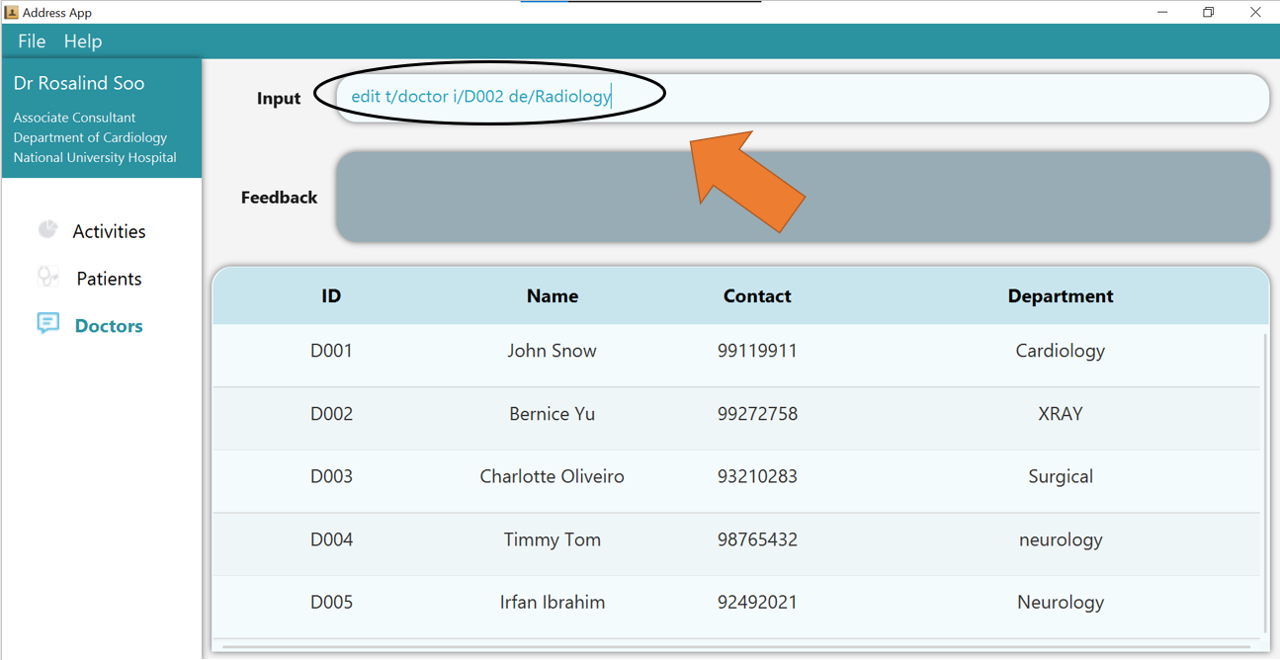
2. Press Enter and the success confirmation should be shown by the feedback box as shown by 1.
As shown by 2, doctor D002, Bernice, has her department updated!
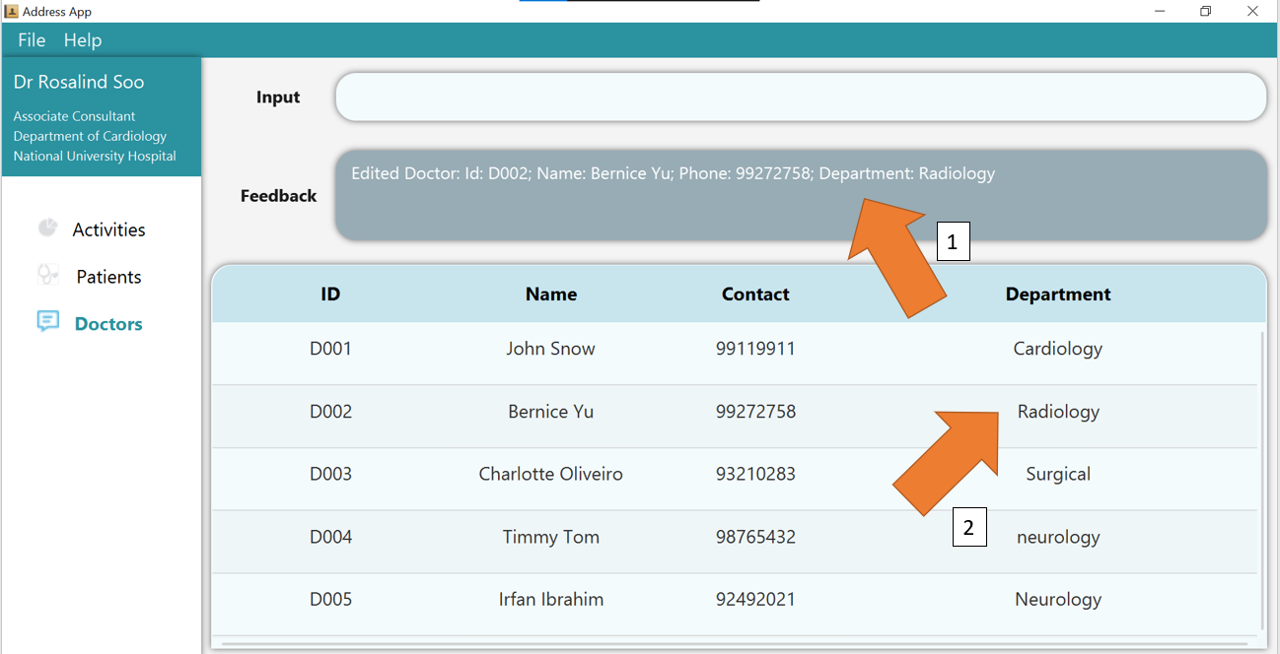
3. If there are any errors, the command would turn red as shown by 1. Also, feedback about the error displayed in the
feedback box, as seen by 2. In this case, the error is that the NAME of the edited doctor contains *, which is an illegal character.
Fix the issue and the command should work correctly now!
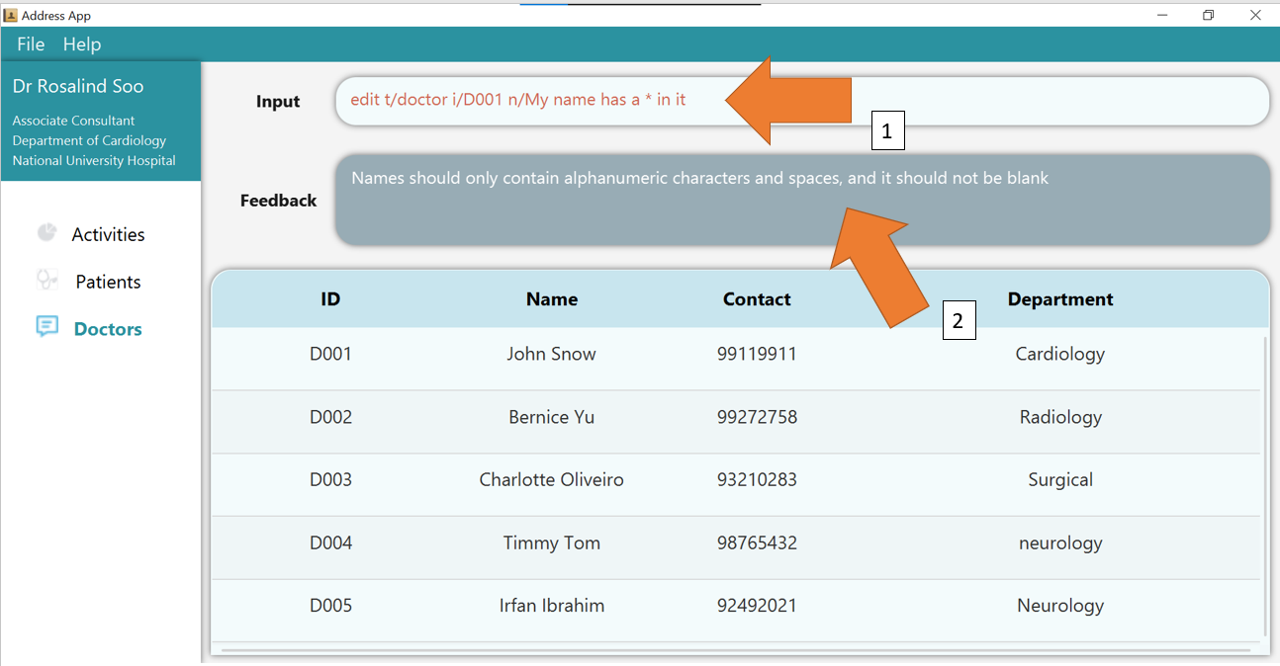
To understand better how GoMedic classifies the error messages, please refer to this section.
3.2.6 Clear all doctor entries: clear t/doctor
Clears all doctor entries from GoMedic.
Format: clear t/doctor
Example:
1. Type the command clear t/doctor into the command box. Press Enter and all the doctors will be deleted.
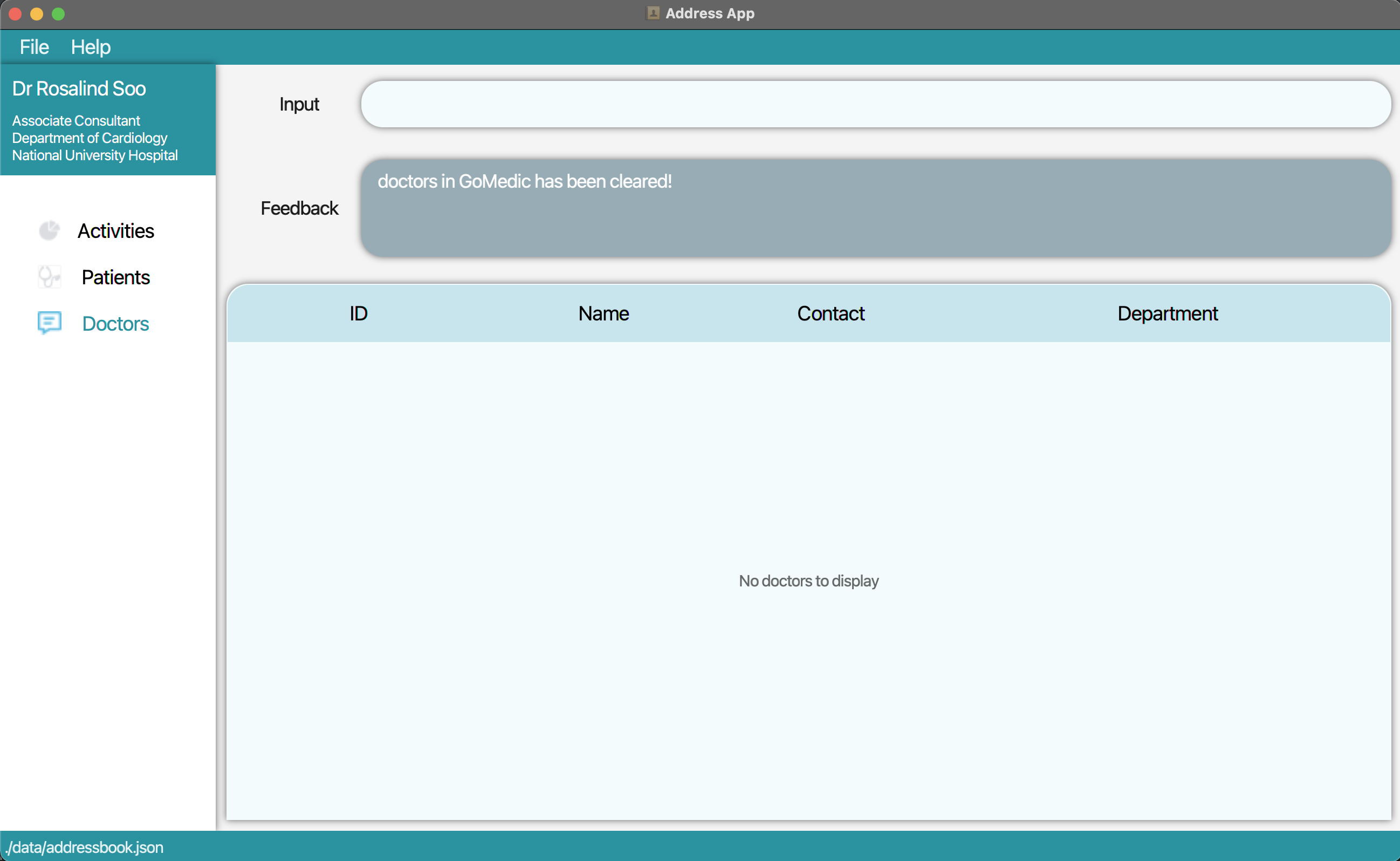
3.3 Activities Related Features
3.3.1 Overview
Activities related features allow you to add, delete, edit and list events and appointments with patients.
Using these activities related features, you can track your daily, weekly or even monthly schedules. GoMedic will also automatically check for any conflicting activities and notify you everytime you try to create a new activity or update an existing activity.
![]() Notes about the Time format:
Notes about the Time format:
- There are three accepted datetime formats (GMT+8 24-Hour Time format):
- dd/MM/yyyy HH:mm (e.g. 15/09/2022 13:00)
- dd-MM-yyyy HH:mm (e.g. 15-09-2022 13:00)
- yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm (e.g. 2022-09-15 13:00)
Each activity is uniquely identified by its ACTIVITY_ID in the form of AXXX where XXX is a 3-digit integer.
Therefore, two activities with exactly same TITLE and DESCRIPTION with different ACTIVITY_ID are considered distinct.
Current Activities Related Features That Are Not Supported by GoMedic
- Creating and editing recurrent events.
- Associating other doctors for an event.
- Listing the activity in a Calendar style.
![]() Reminder on Command Notation:
Reminder on Command Notation:
- Some important notation in reading the commands
-
[flag/KEYWORD]indicates optional parameters -
flag/KEYWORDindicates mandatory parameters
-
3.3.2 Adding a new activity: add t/activity
Adds a new activity into your GoMedic scheduler.
Format: add t/activity s/START_TIME e/END_TIME ti/TITLE [d/DESCRIPTION]
GoMedic will create a new activity based on the smallest ACTIVITY_ID available. This example is shown here, where
a new activity added is assigned the ID A006 instead of A008. This means that this new activity is not displayed as the last entry in the list,
as the table is sorted by ACTIVITY_ID by default.
- GoMedic will check for any partial or fully conflicting activities and notify you immediately if there are any. Should there be any, the new activity will not be added.
- GoMedic will also check for any invalid parameters as specified here. Should there be any, the new activity will not be added.
The parameters are:
| Parameters | Explanation | Constraints |
|---|---|---|
s/START_TIME |
the starting time of the appointment. | Should be a valid datetime in a valid format specified here |
e/END_TIME |
the ending time of the activity. | Should be a valid datetime in a valid format specified here |
ti/TITLE |
the title of the activity. | maximum of 60 characters |
d/DESCRIPTION |
the description of the activity. | maximum of 500 characters |
![]() Extra Constraints
Extra Constraints
-
START_TIMEmust be strictly less thanEND_TIME. -
Activities with partially overlapping times are still considered as conflicting activities.
Example:
1. Type the command add t/activity s/2022-09-15 14:00 e/15/09/2022 15:00 ti/Meeting with Mr. X d/about a certain paper into
the command box.
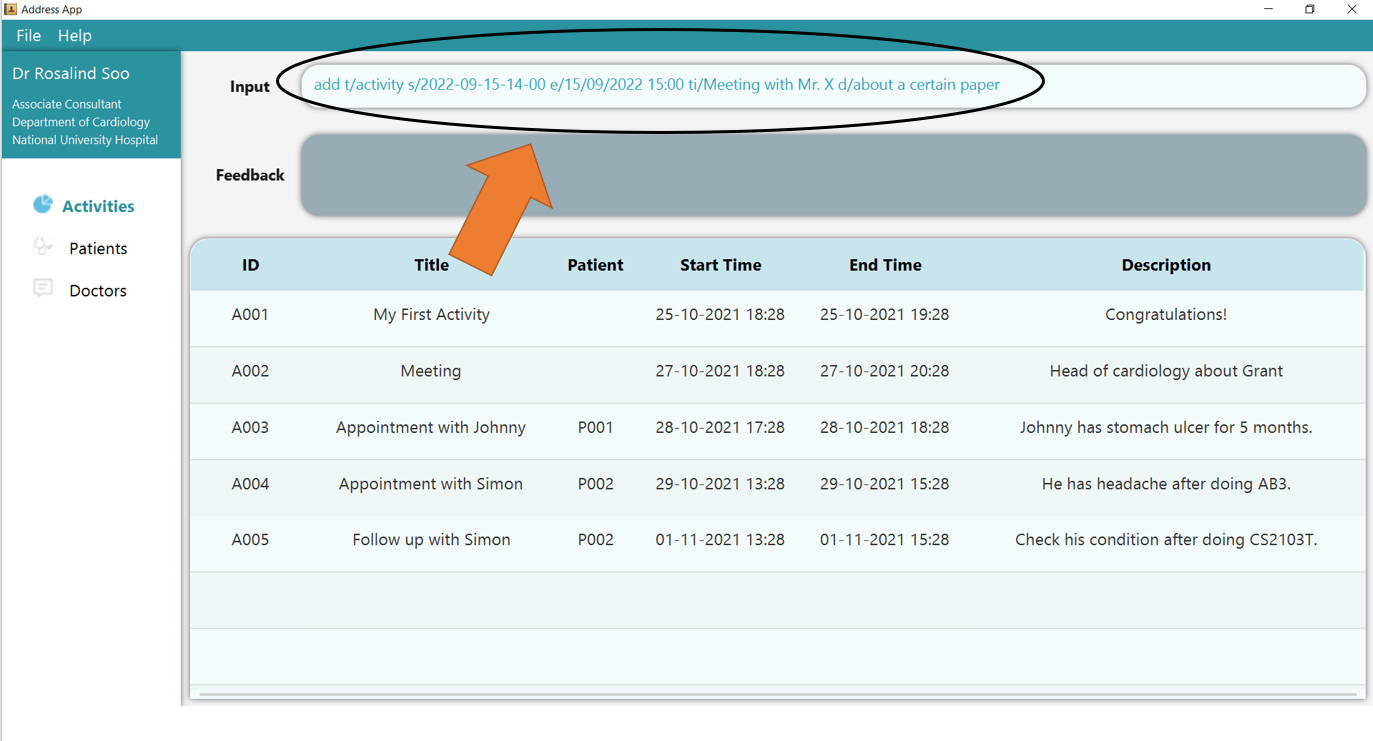
2. Press Enter and you should see the new entry being made in the Activity table! By default, the table would be sorted by ID.
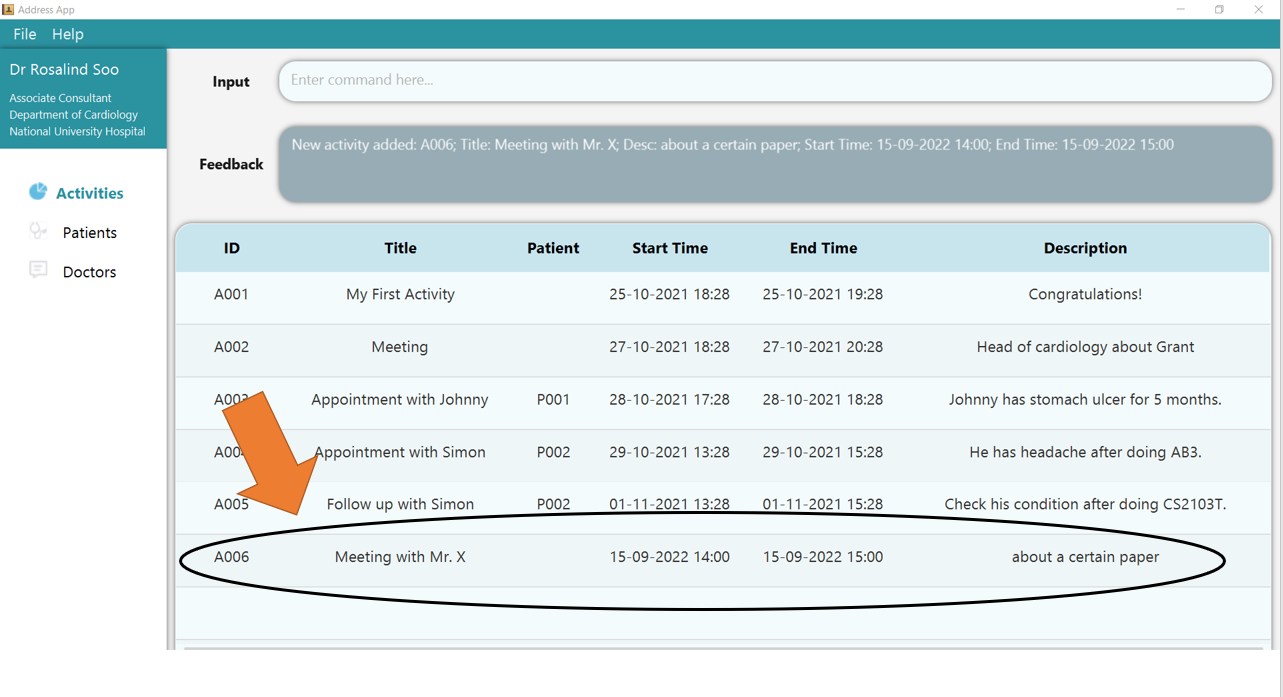
3. If there are any errors, the command would turn red as indicated by 1 and feedback would be given in the feedback box, as seen by 2.
In this case, the error caused by an invalid time format, in the form 2022-09-15-14-00, being supplied to START_TIME. Fix the issue and press enter again!
Now the command should work correctly!
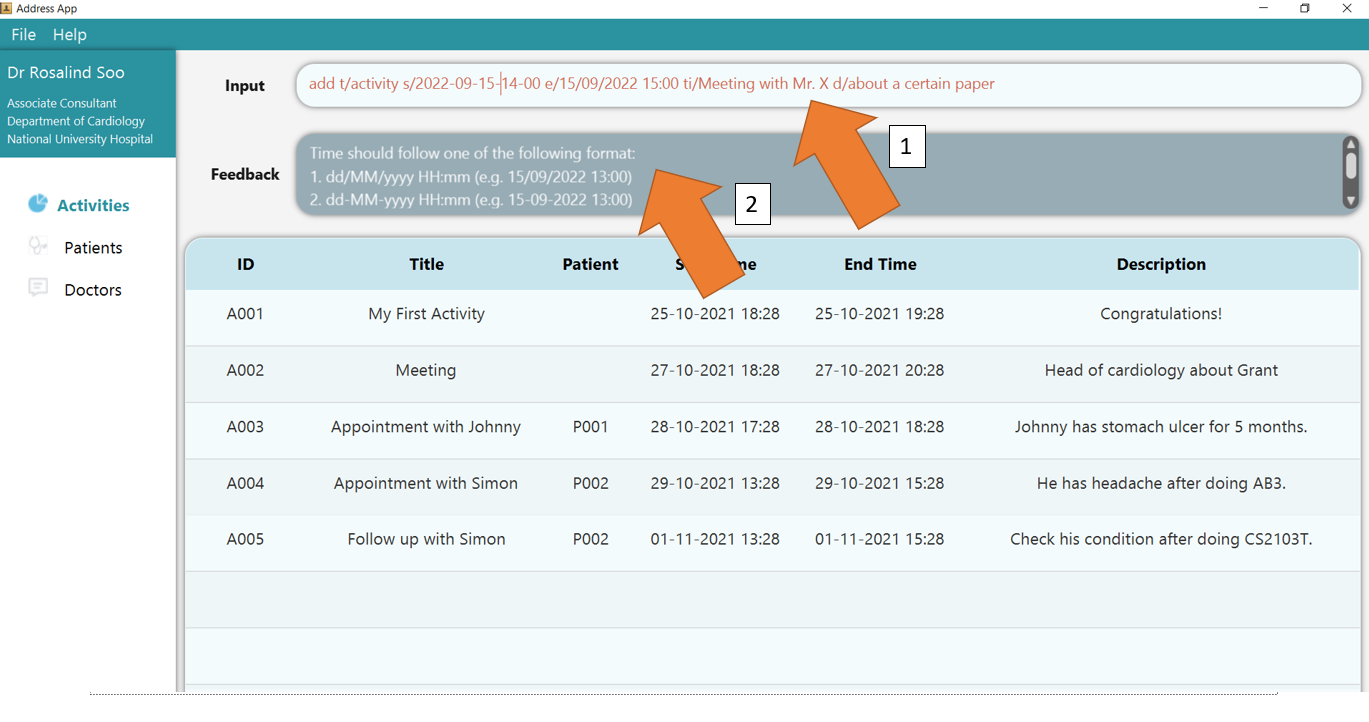
To understand better how GoMedic classifies the error messages, please refer to this section.
3.3.3 Adding a new appointment: add t/appointment
Adds a new appointment into your GoMedic scheduler.
Format: add t/appointment i/PATIENT_ID s/START_TIME e/END_TIME ti/TITLE [d/DESCRIPTION]
An Appointment is a type of Activity, with an additional parameter PATIENT_ID associated with it. Currently, GoMedic only supports
one-to-one appointments. Besides the checks performed on usual activity, GoMedic would also check
- if the Patient identified by his/her
PATIENT_IDexists. If not, GoMedic will immediately notify the user and the new appointment will not be added to the list.
The parameters are:
| Parameters | Explanation | Constraints |
|---|---|---|
i/PATIENT_ID |
the Patient Id associated with the appointment | Patient Id must in the form of PXXX / pXXX, where XXX is 3 digit number |
s/START_TIME |
the starting time of the appointment. | Should be a valid datetime in a valid format specified here |
e/END_TIME |
the ending time of the activity. | Should be a valid datetime in a valid format specified here |
ti/TITLE |
the title of the activity. | maximum of 60 characters |
d/DESCRIPTION |
the description of the activity. | maximum of 500 characters |
The activity constraints are still applicable here.
1. Type the command add t/appointment i/P001 s/2022-09-15 14:00 e/15/09/2022 15:00 ti/Appointment with Patient X into
the command box.
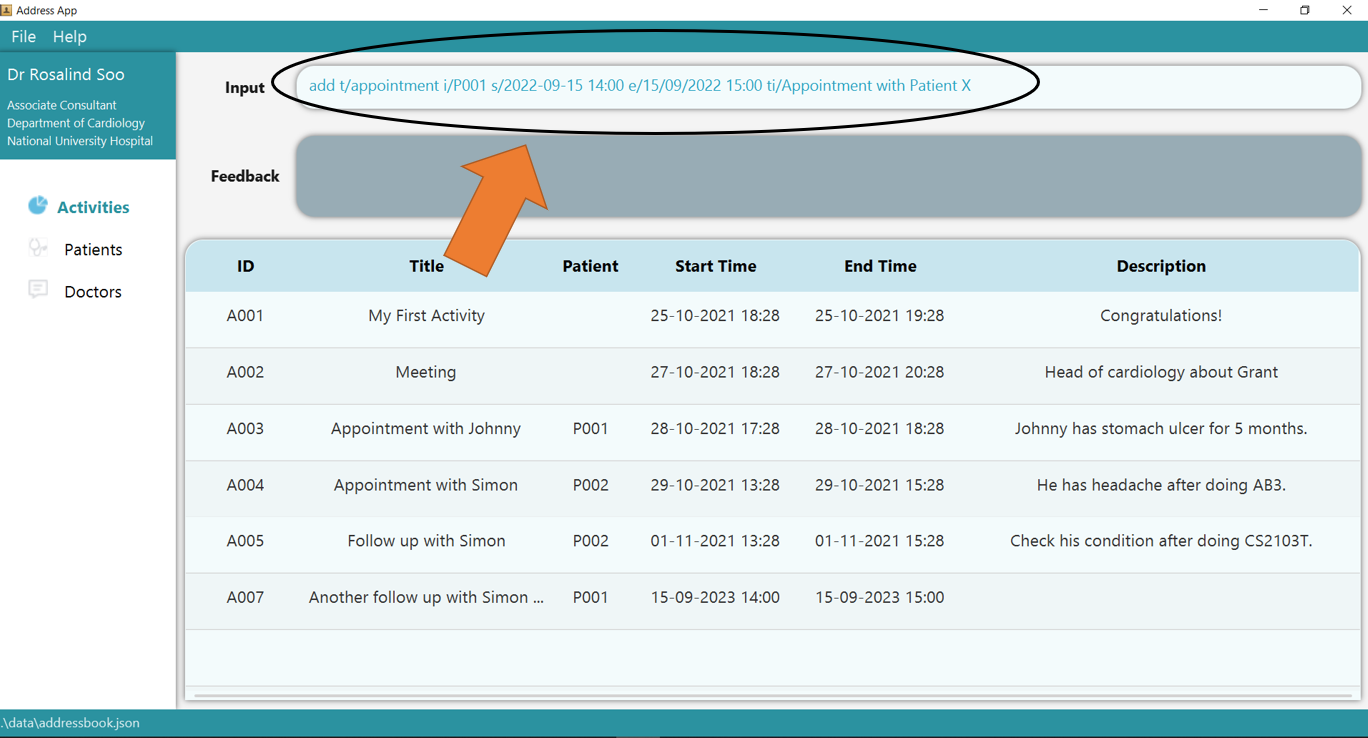
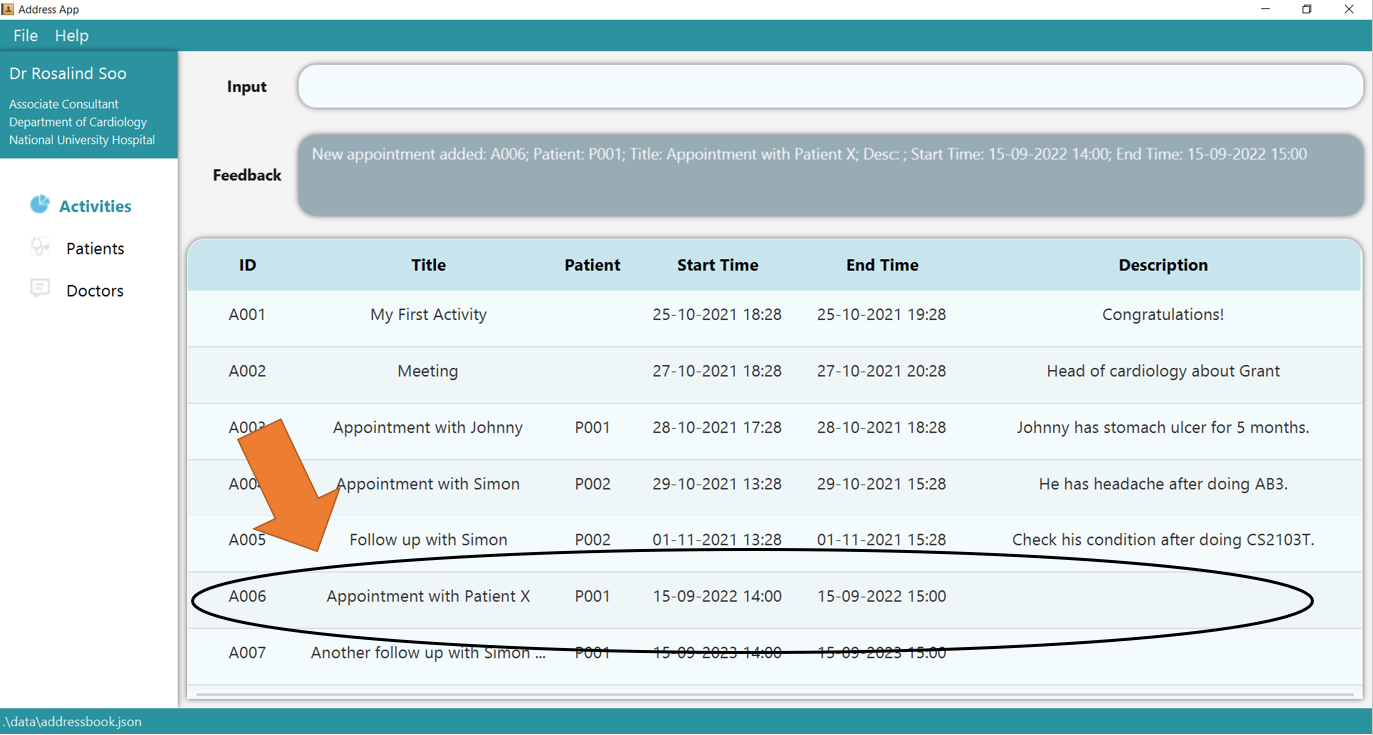
2. Press Enter and you should see the new entry being made in the Activity table! By default, the table would be sorted by ID. Hence, note that
the new entry is not displayed as the last entry!
3. If there are any errors, the command will turn red as shown by 1.
Furthermore, if the patient does not exist, as shown by 2, the user needs to create the patient first, using the add t/patient command.
Fix the issue and press Enter again, the command should work correctly now!
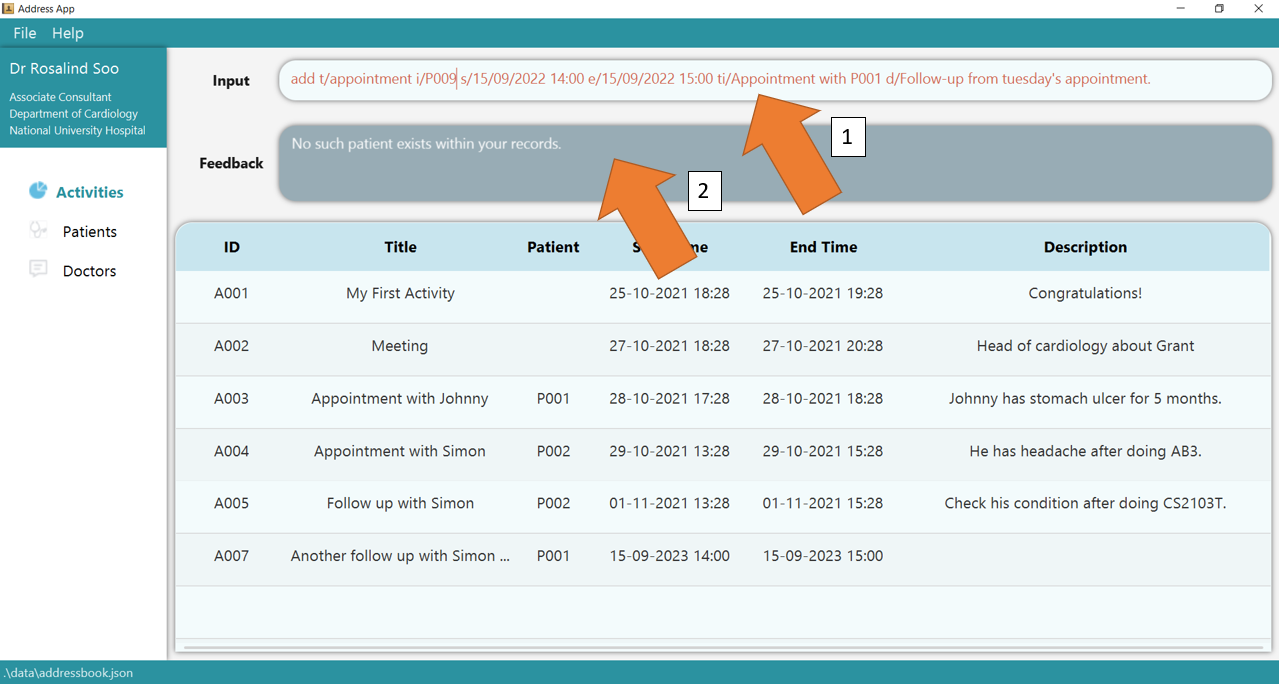
To understand better how GoMedic classifies the error messages, please refer to this section.
3.3.4 Deleting an existing activity: delete t/activity
Delete an existing activity from GoMedic.
Format: delete t/activity ACTIVITY_ID
ACTIVITY_ID does not require additional flags such as i/! Supplying those flags would render the command invalid!
The parameter is:
| Parameter | Explanation | Constraint |
|---|---|---|
ACTIVITY_ID |
the Activity Id as shown by the Activity table (case-insensitive) | Must be in the form of AXXX / aXXX where XXX is 3-digit integer. For the full information, please refer to this
|
ACTIVITY_ID can be obtained by listing all the activities using list t/activity command
or searching for the specific activity using find t/activity command.Example:
1. Type the command delete t/activity A001 into the command box.
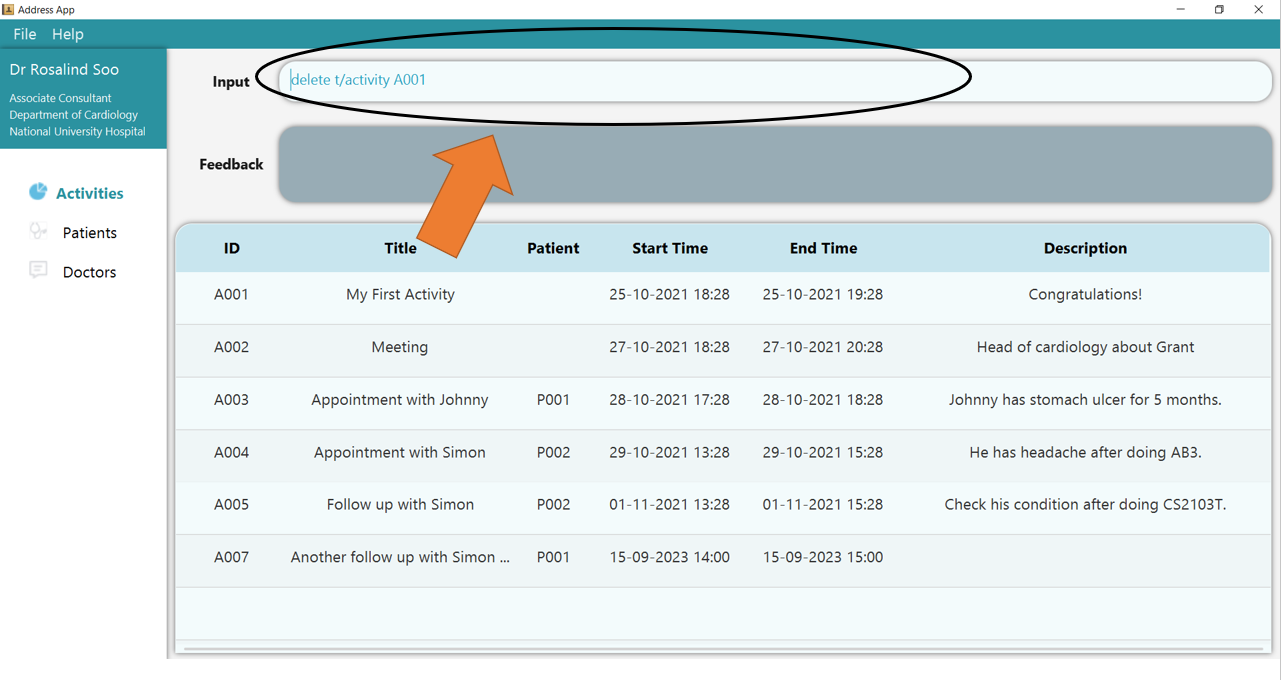
2. Press Enter and you will get confirmation that the activity is indeed deleted. Check the activity table. The activity, identified by its deleted ID, should not be there.
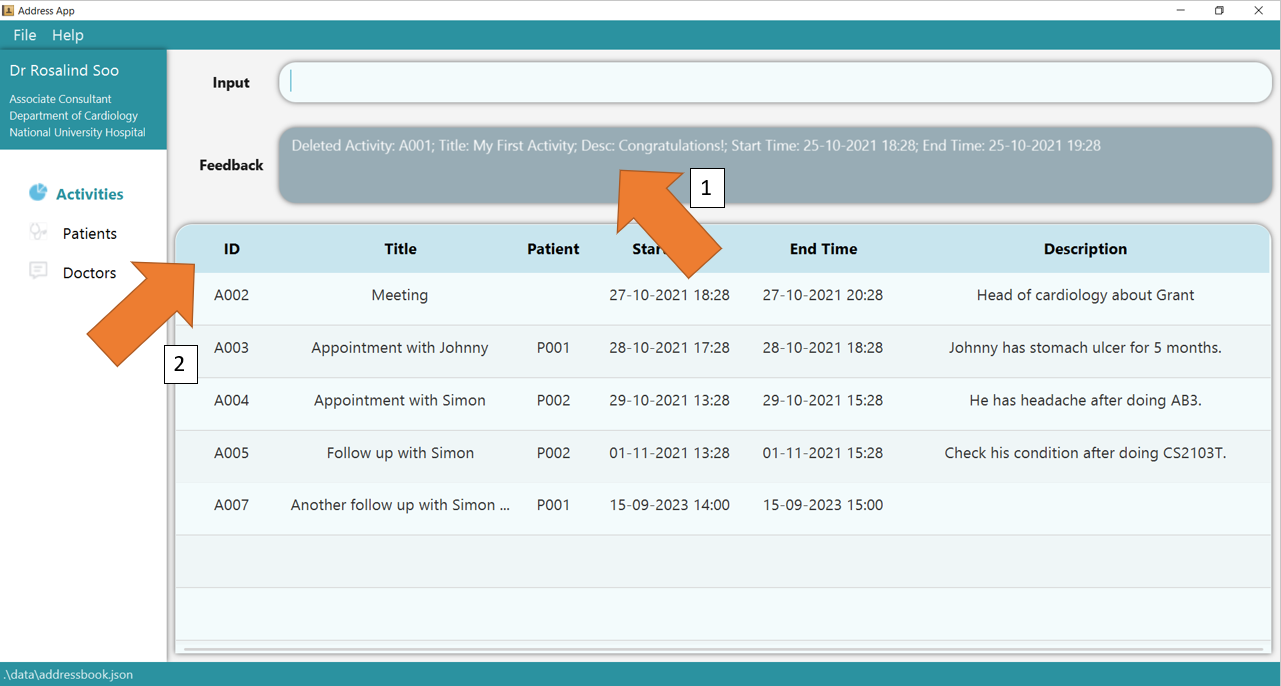
3. If there are any errors, the command will turn red as shown by 1. Also, feedback about the error is displayed in the feedback box, as seen by 2. Fix the issue and the command should work correctly now!
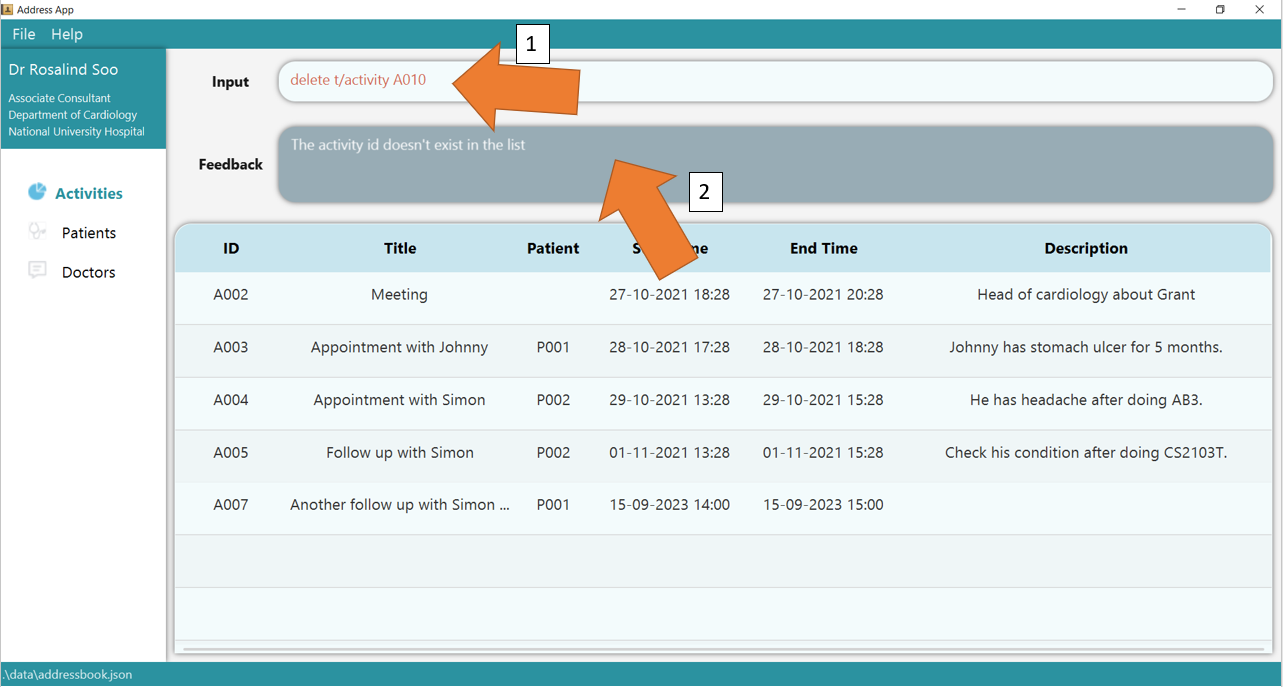
To understand better how GoMedic classifies the error messages, please refer to this section.
3.3.5 List all activities: list t/activity
Lists all activities that is stored in GoMedic.
Format: list t/activity s/SORT_FLAG p/PERIOD_FLAG
By default, all activities will be displayed in ascending order of ID.
- Regardless on the input format of the
START_TIMEandEND_TIMEfield, it will be displayed indd-MM-yyyy HH:mmGMT+8 24-Hour format. - Titles and Descriptions that are too long will be truncated.
The parameters are :
| Parameters | Explanation | Constraints |
|---|---|---|
s/SORT_FLAG |
Options to sort the activity table by a certain column (case-insensitive) | - START : sort by start time - ID : sort by ID |
p/PERIOD_FLAG |
Options to show the activities within the specified time frame (case-insensitive) | - ALL : show all activities - TODAY : show today’s activities - WEEK : show all activities within the next week - MONTH : show all activities within the next month - YEAR : show all activities within the next year |
Example:
1. Type the command list t/activity p/today into the command box. In this example, today refers to the date 28 October 2021. Note that the flag is case-insensitive!
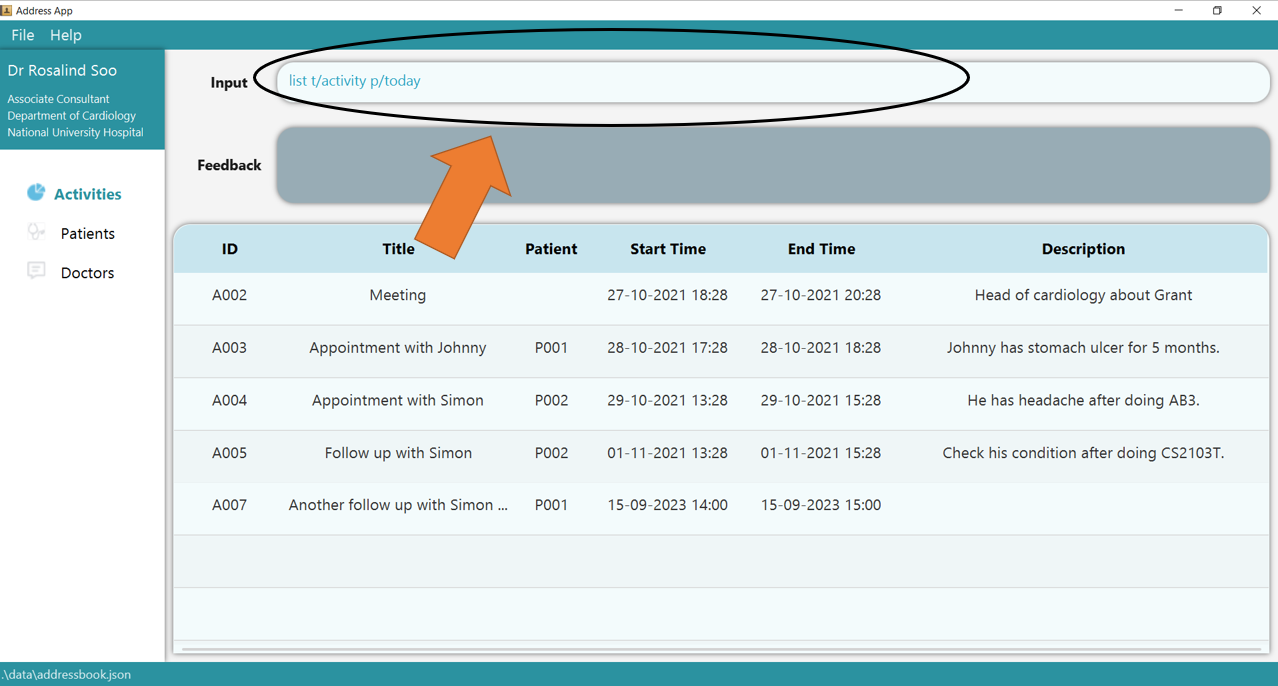
2. Press Enter and the success confirmation should be shown by the feedback box as shown by 1. As shown by 2, the activity table only shows today’s activities.
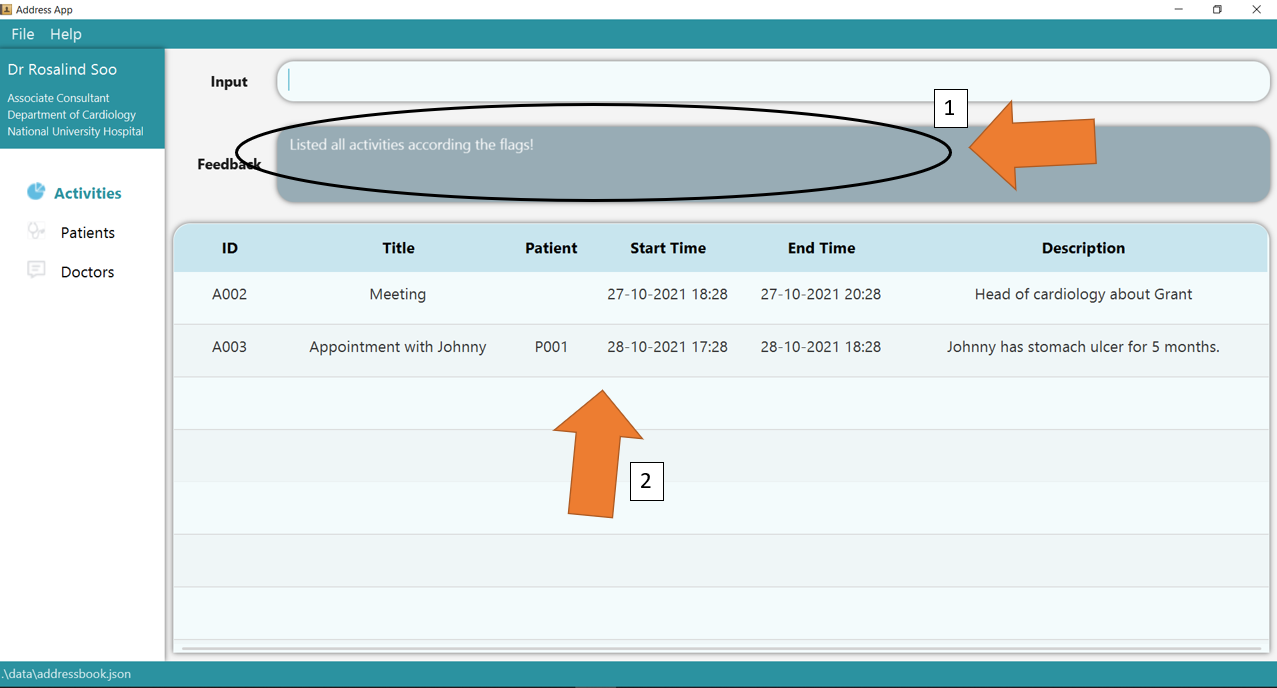
3. If there are any errors, the command will turn red as shown by 1. Also, feedback about the error is displayed in the feedback box, as seen by 2. Check that the flags supplied are only from the list of available ones specified in constraints above! Fix the issue and the command should work correctly now!
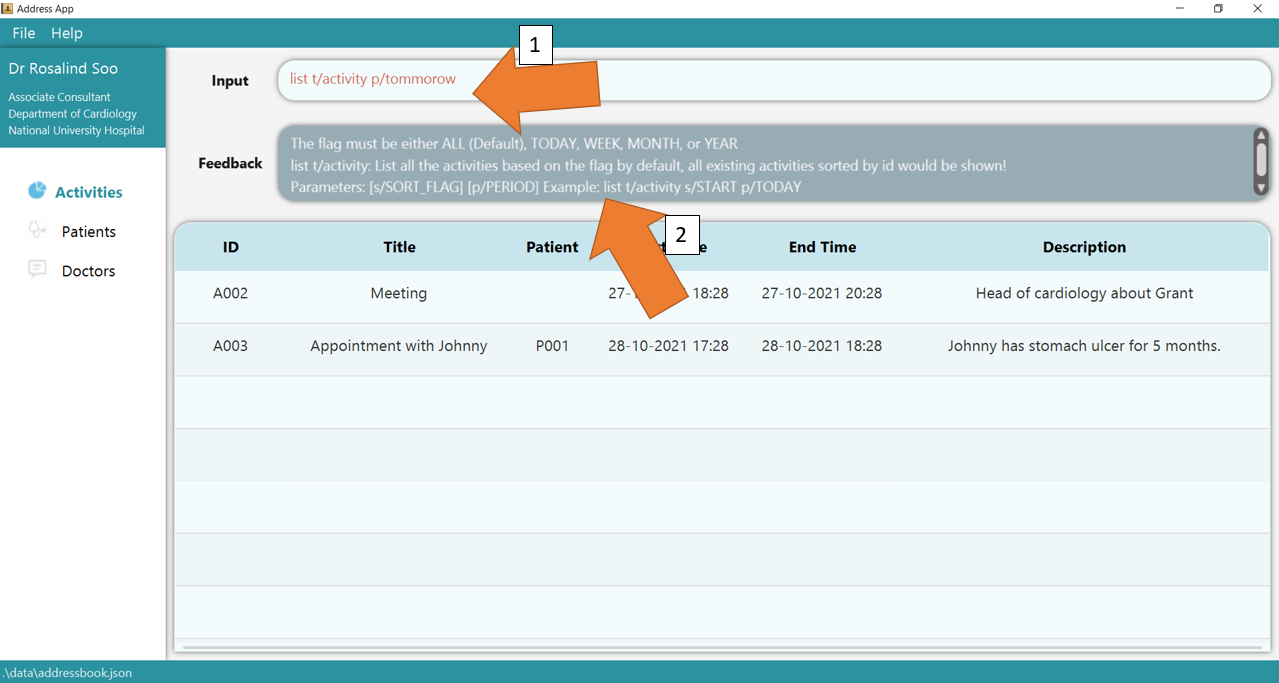
To understand better how GoMedic classifies the error messages, please refer to this section.
3.3.6 Updating an existing activity’s details: edit t/activity
Edits an activity’s details from the GoMedic application.
Format: edit t/activity i/ACTIVITY_ID [OPTIONAL PARAMETERS]...
When editing an existing activity, all parameters are optional except ACTIVITY_ID! However,
- If there are no parameters being supplied other than
ACTIVITY_ID, GoMedic will return an error. -
GoMedic will check for any conflicting activities when the
START_TIMEor theEND_TIMEis modified.
![]() Caution:
Caution:
- The
PATIENT_IDof an appointment cannot be modified! You need to delete and create a new appointment to modify thePATIENT_ID - The
ACTIVITY_IDis also assigned by GoMedic and cannot be modified at all once created.
The parameters are:
| Parameters | Explanation | Constraints |
|---|---|---|
i/ACTIVITY_ID |
the unique identifier of an activity (case-insensitive). | Must be in the form of AXXX / aXXX where XXX is 3-digit integer. For full info, please refer to this
|
s/START_TIME |
the starting time of the appointment. | Should be a valid datetime in a valid format specified here |
e/END_TIME |
the ending time of the activity. | Should be a valid datetime in a valid format specified here |
ti/TITLE |
the title of the activity. | maximum of 60 characters |
d/DESCRIPTION |
the description of the activity. | maximum of 500 characters |
Example:
1. Type the command edit t/activity i/A002 ti/My Edited Activity into the command box. Ensure that the edited activity, as identified by its ACTIVITY_ID, exists!
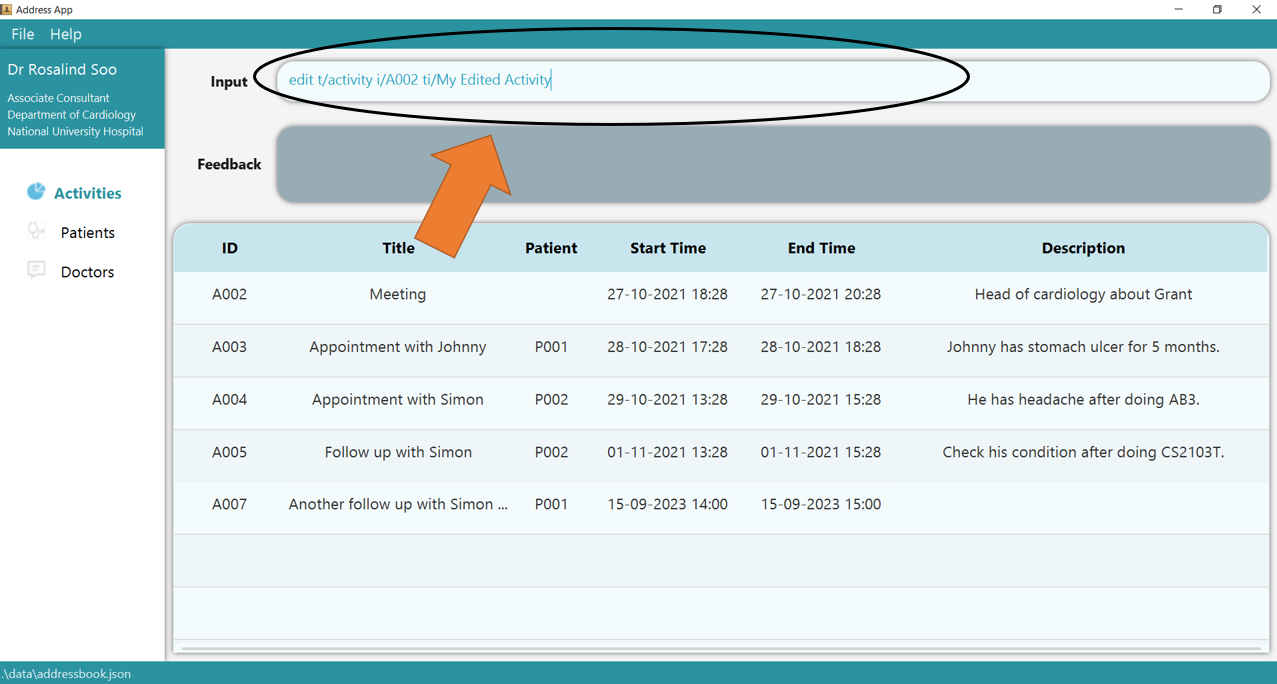
2. Press Enter and the success confirmation should be displayed in the feedback box, as seen by 1. As shown by 2, activity A002 has its title updated!
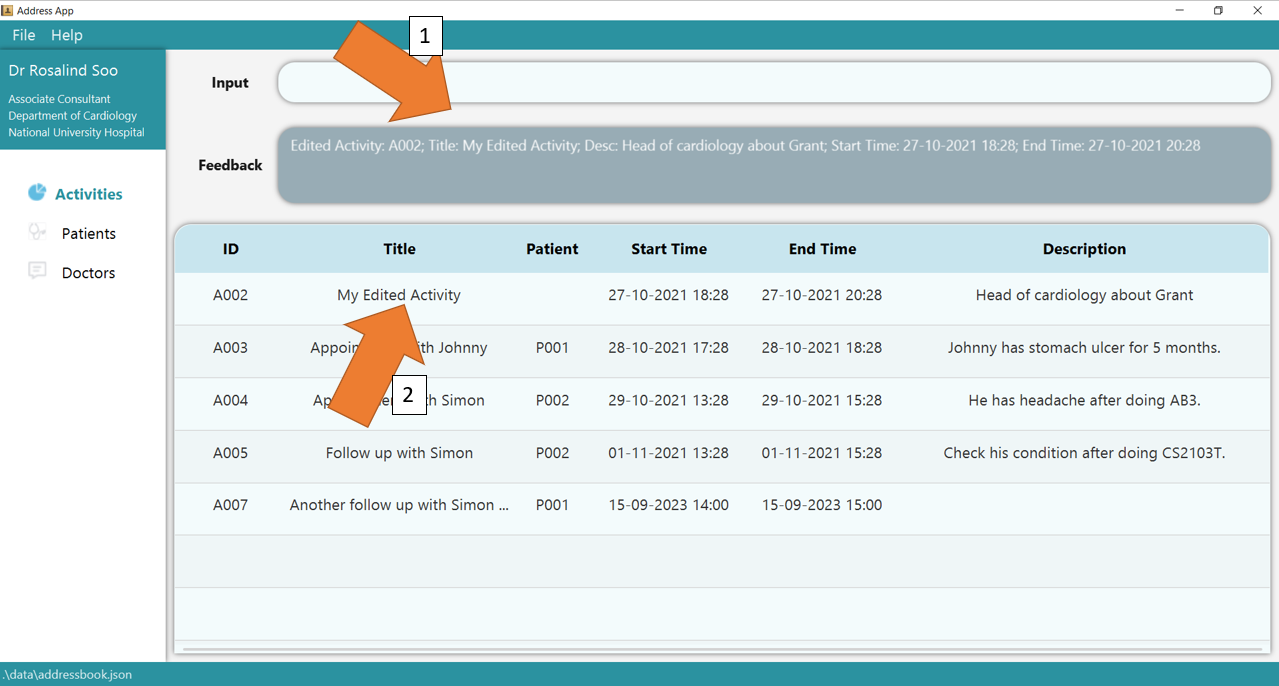
3. If there are any errors, the command will turn red as shown by 1. Also, feedback about the error is displayed in the
feedback box shown at 2. In this case, the error is that START_TIME of the edited activity is later than its END_TIME. Fix the issue and the command should work correctly now!
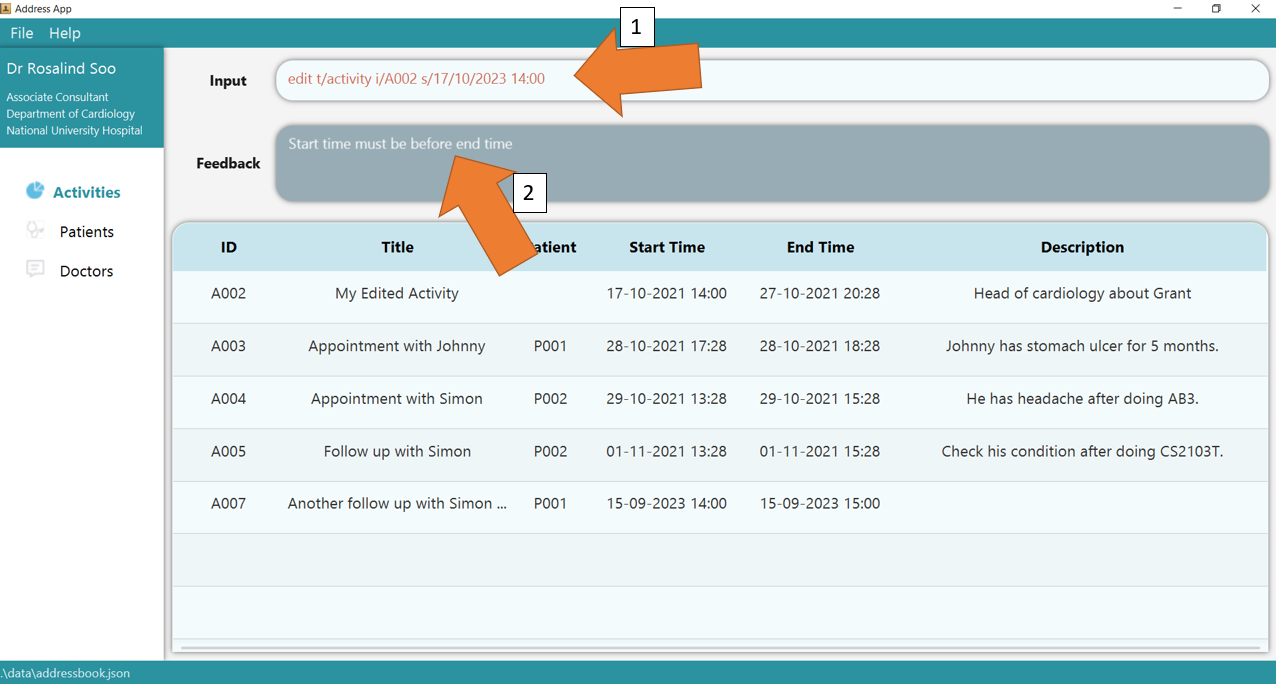
To understand better how GoMedic classifies the error messages, please refer to this section.
3.3.7 Clear all activity and appointment entries: clear t/activity
Clears all activities and appointment entries from GoMedic.
Format: clear t/activity
Example:
1. Type the command clear t/activity into the command box. Press Enter and all the appointments and activities will be deleted.
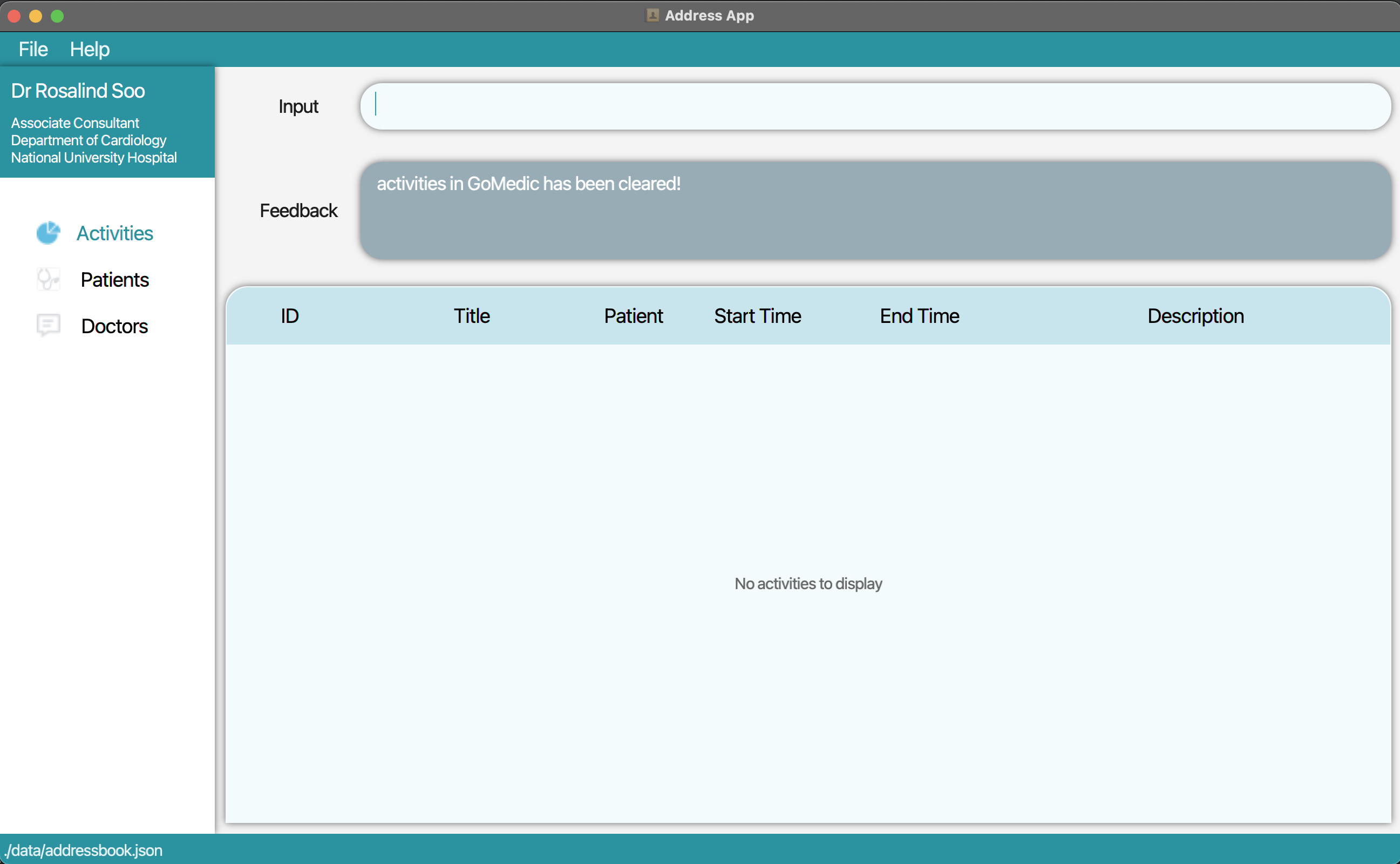
3.4. Finding entries
3.4.1 Overview
The find feature allows you to search for entries based on user input by matching the input string with the user-specified fields.
The model that is being searched must be specified too - doctor, patient or activity.
For all find functions, the Keyword is case-insensitive for convenience (“dia” will match diabetic patients even if the user stored the patient’s condition as “Diabetes”)
The keywords entered will be separated by spaces and each word will be checked against the specified field to see if there is a match.
A match, in this context, is defined by when the specified field contains a word from the keywords, as a substring.
For example, find t/doctor n/bo yang lim will return doctors with names containing bo or yang or lim.
The constraints of the field are not checked with the user input. For example, if the user enters
find t/doctor p/hello, GoMedic will not throw an error saying that phone number must be
8 digits only. GoMedic will simply display that there are no matching entries where the phone number
field in a doctor contains hello.
3.4.2 Finding a doctor through a keyword find t/doctor
Searches for doctors whose specified field contains one or more of the specified keywords as a substring.
Format: find t/doctor FIELD/[KEYWORDS]
GoMedic will display the matching doctors.
The possible parameters for FIELD are:
| Parameters | Explanation |
|---|---|
n/NAME |
Matches the name of the doctor |
p/PHONE_NUMBER |
Matches the phone number of the doctor |
de/DEPARTMENT |
Matches the department of the doctor |
Example:
1. Clear the entire doctor table using clear t/doctor and type the command find t/doctor n/Hans Bo. Since there are no doctors yet
(or whenever none of the doctors match the queries), the following page will be shown.
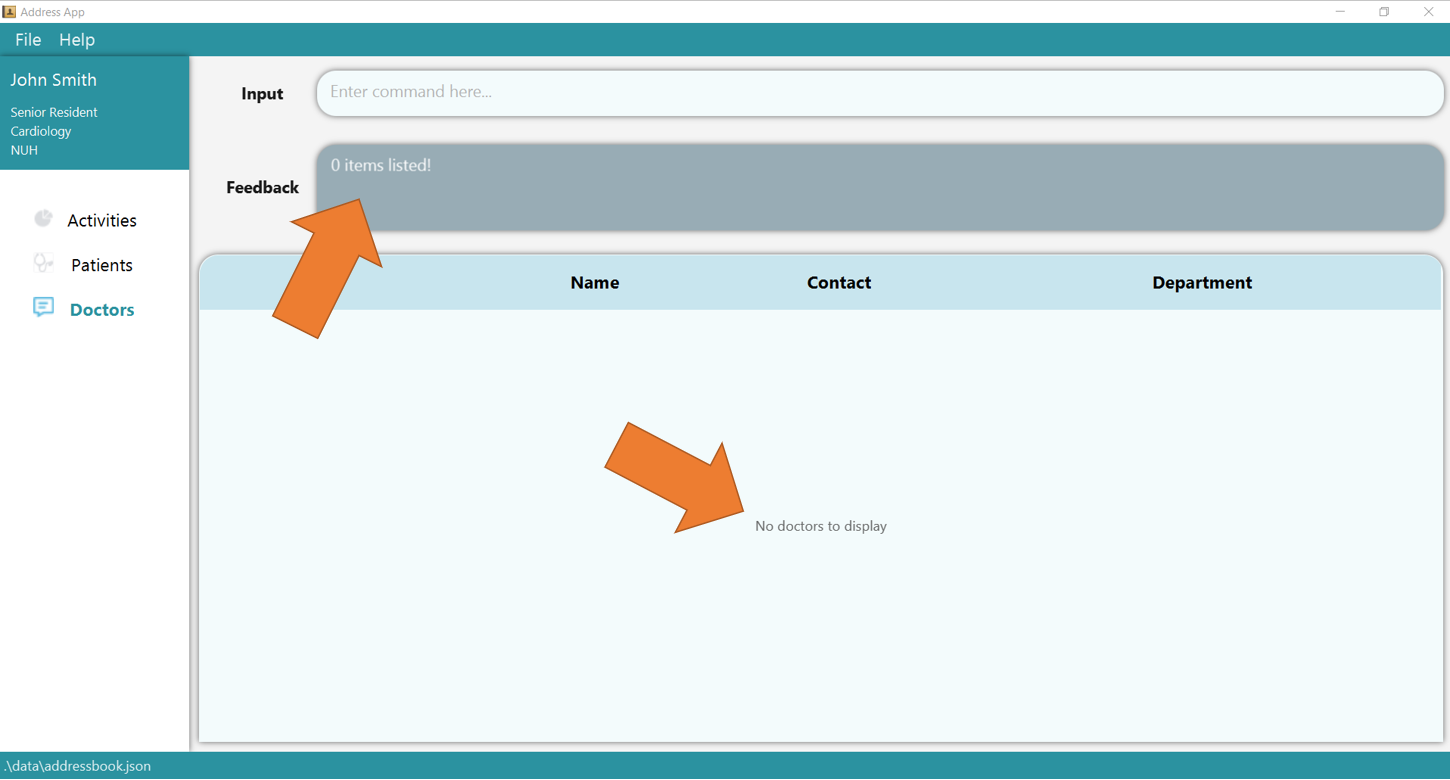
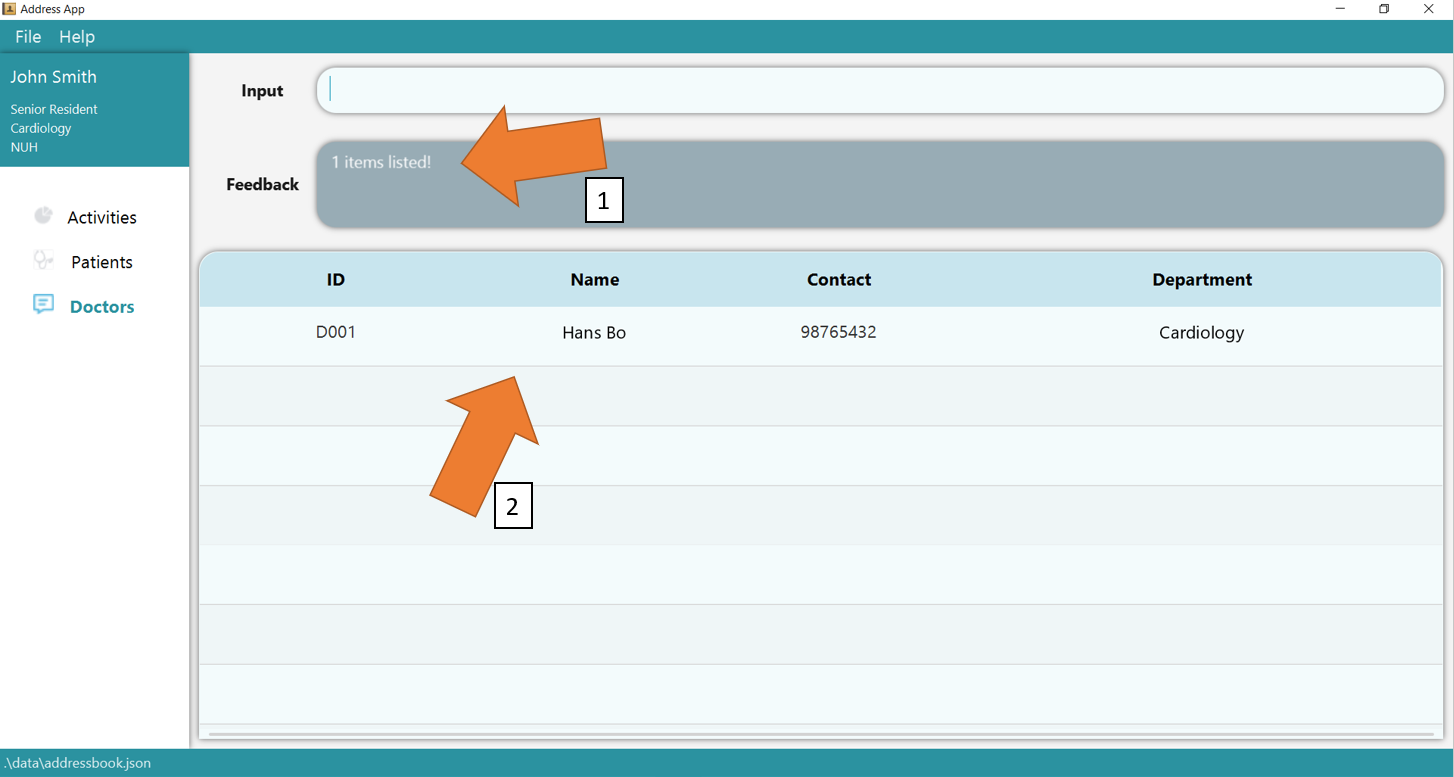
2. Now add 2 new doctors using add t/doctor n/Hans Bo p/98765432 de/Cardiology and add t/doctor n/Yang Bo p/99991234 de/Dermatology.
Ensure they are added by using list t/doctor command. To find the doctor whose name contains “Hans”, simply type the command find t/doctor n/Hans again.
GoMedic would show number of matching records as shown in 1 and display them in the table as shown in 2.
3. If there is any invalid parameters supplied, for e.g. more than 2 fields are supplied, GoMedic will make the commands turn red as shown in 1 and would display the feedback as shown in 2.
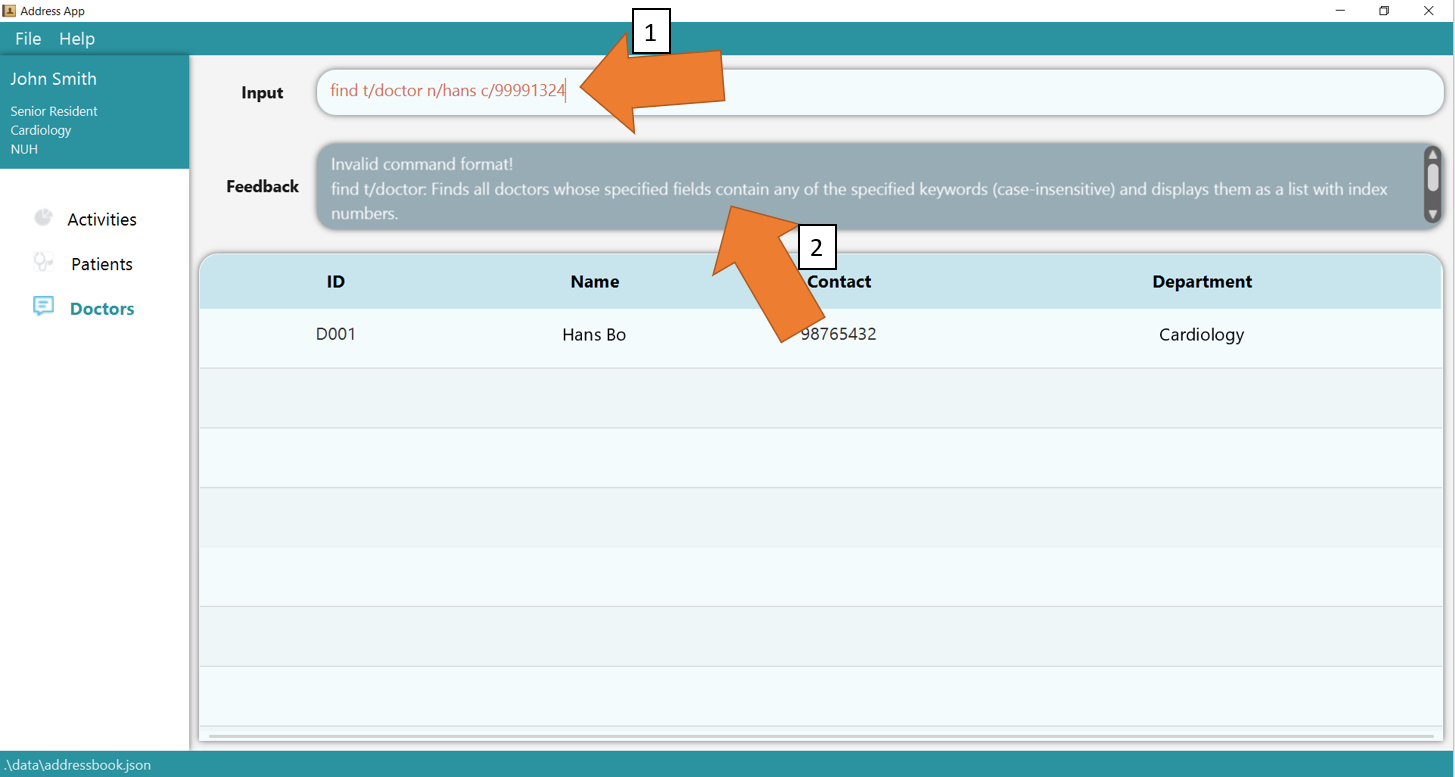
To understand better how GoMedic classifies the error messages, please refer to this section.
3.4.3 Finding a patient through a keyword find t/patient
Searches for patients whose specified field contains one or more of the specified keywords as a substring.
Format: find t/patient FIELD/[KEYWORDS]
GoMedic will display the matching patients.
The possible parameters for FIELD are:
| Parameters | Explanation |
|---|---|
n/NAME |
Matches the name of the patient |
p/PHONE_NUMBER |
Matches the phone number of the patient |
a/AGE |
Matches the age field |
g/GENDER |
Matches the gender of the patient |
h/HEIGHT |
Matches the height of the patient in centimeters |
w/WEIGHT |
Matches the weight of the patient in kilograms |
b/BLOOD_TYPE |
Matches the blood type of the patient |
m/MEDICAL_CONDITION |
Matches the medical conditions of the patient |
Example:
1. Clear the entire patient table using clear t/patient and type the command find t/patient n/Hans Bo. Since there are no patients yet
(or whenever none of the patients match the queries), the following page will be shown.
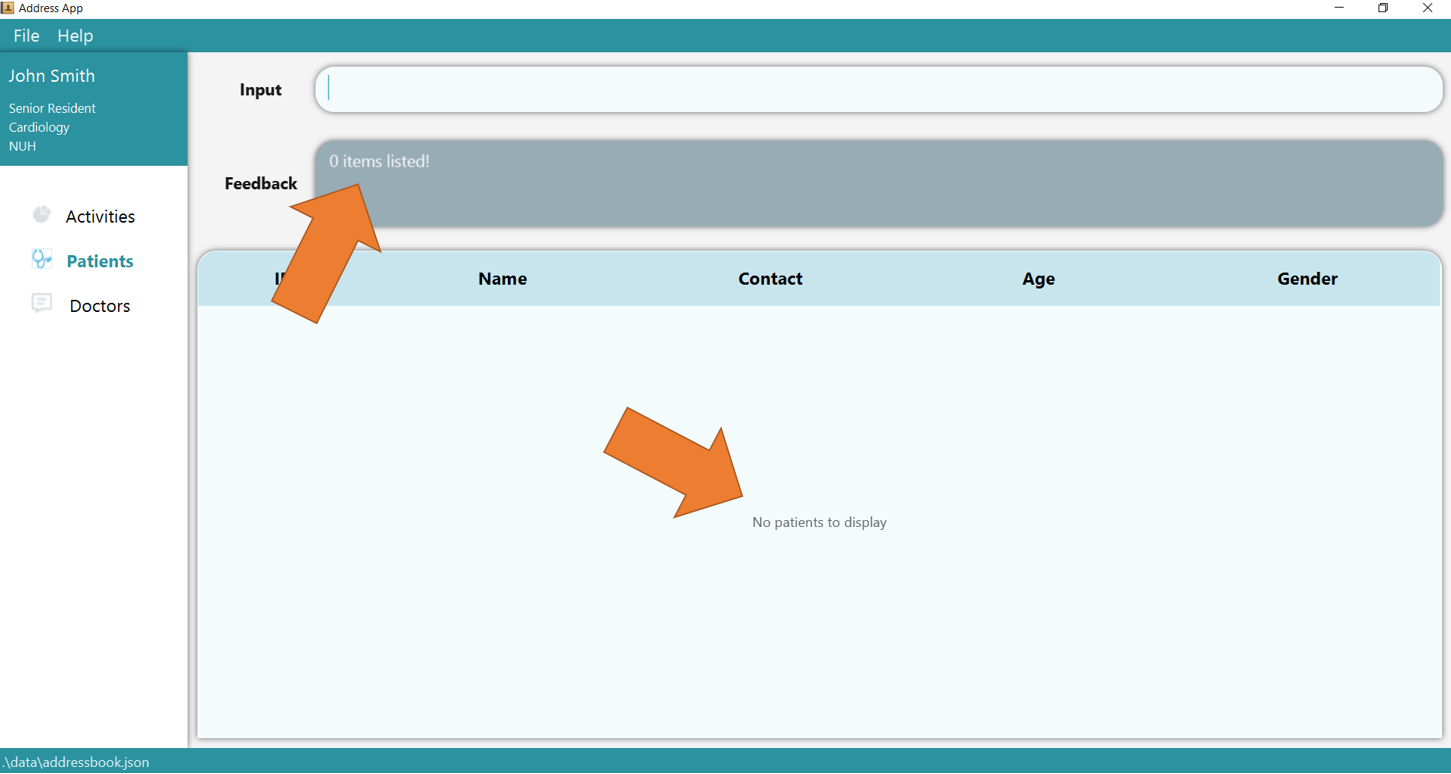
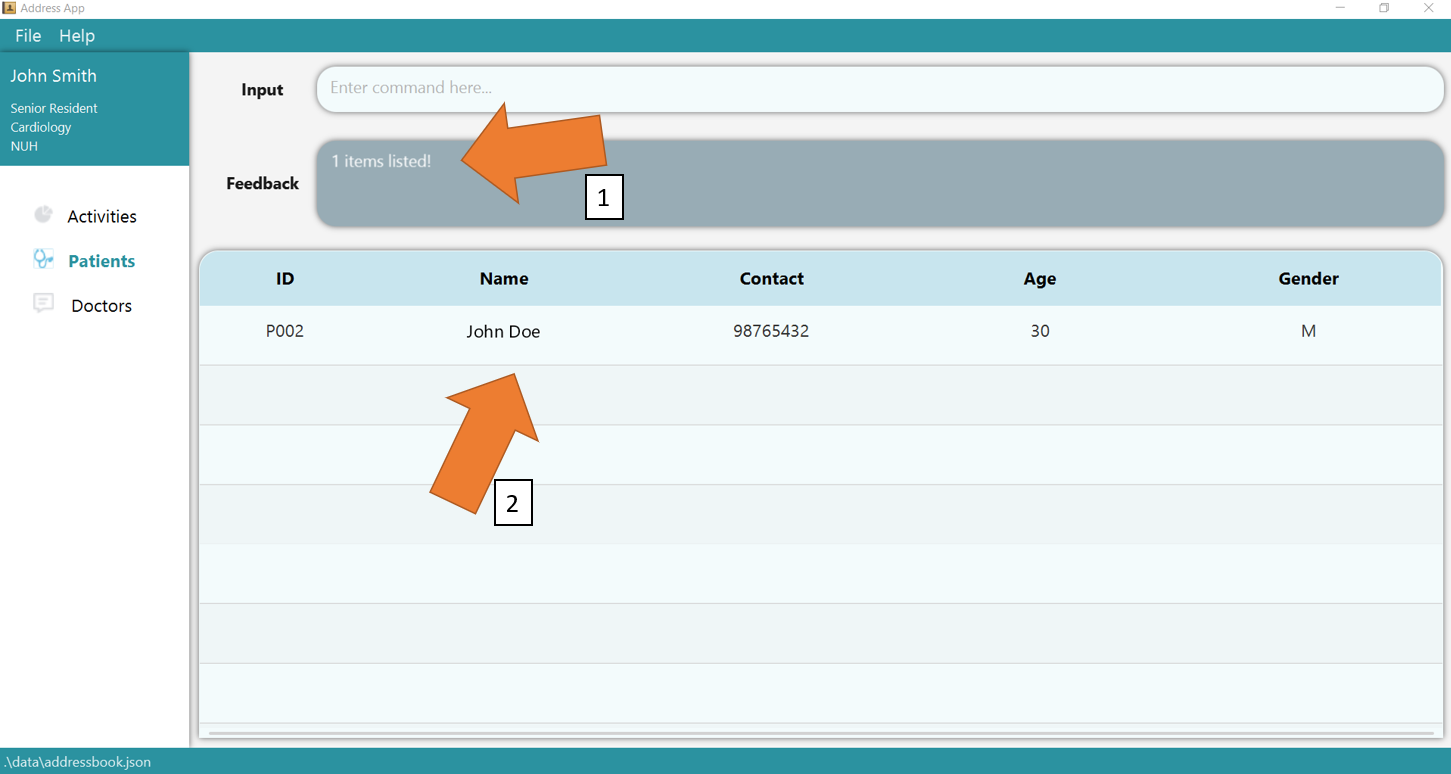
2. Now add 2 new patients using add t/patient n/John Smith p/98765432 a/45 b/AB+ g/M h/175 w/70 m/heart failure m/diabetes and add t/patient n/John Doe p/98765432 a/30 b/O+ g/M h/160 w/90 m/diabetes.
Ensure they are added by using list t/patient command. To find the patient whose blood type is O+, simply type the command find t/patient b/O+ again.
GoMedic would show number of matching records as shown in 1 and display them in the table as shown in 2. You can use view t/patient
to verify the result.
3. If there is any invalid parameters supplied, for e.g. more than 2 fields are supplied, GoMedic will make the commands turn red as shown in 1 and would display the feedback as shown in 2.
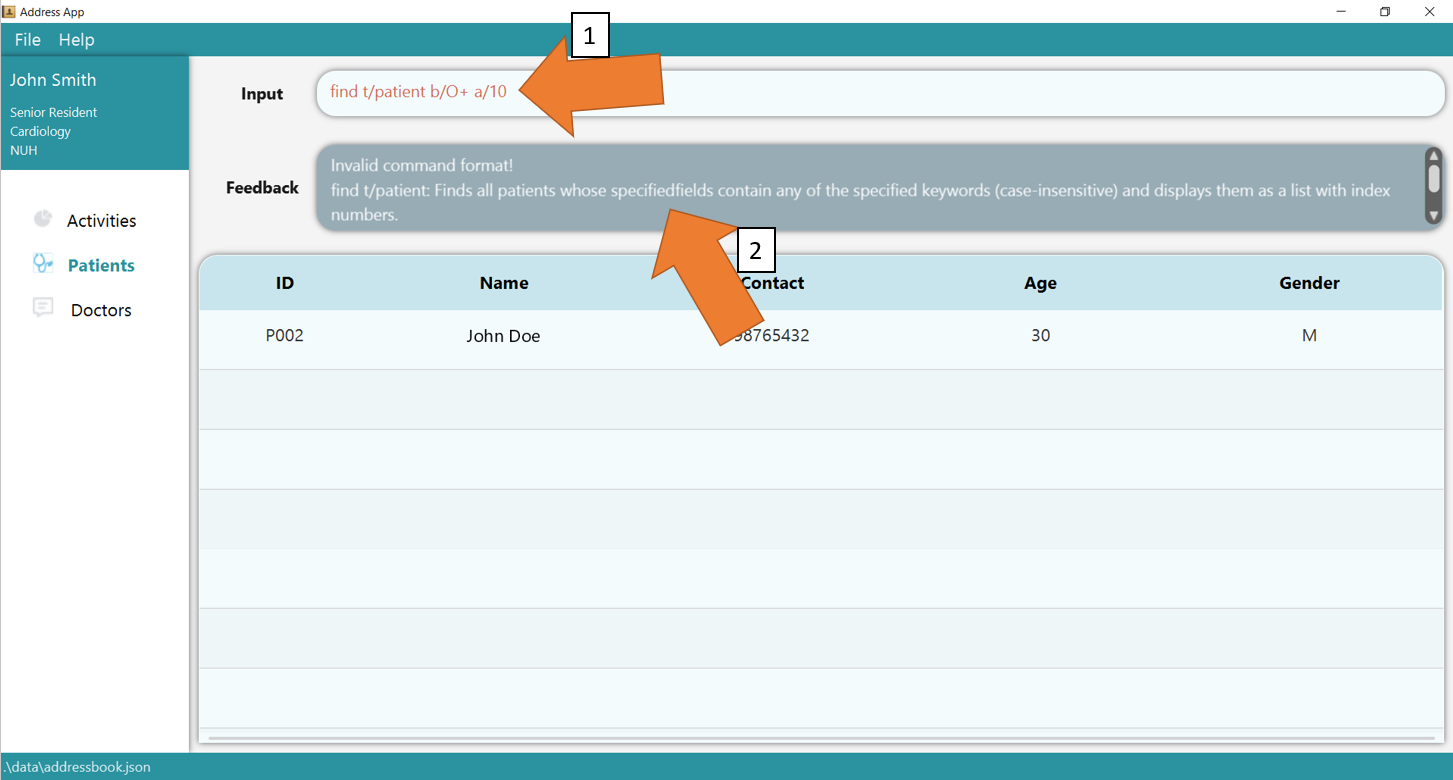
To understand better how GoMedic classifies the error messages, please refer to this section.
3.4.4 Finding an activity through a keyword find t/activity
Searches for activities whose specified field contains one or more of the specified keywords as a substring.
Format: find t/activity FIELD/[KEYWORDS]
GoMedic will display the matching activities.
The possible parameters for FIELD are:
| Parameters | Explanation |
|---|---|
ti/TITLE |
Matches the title field or description field |
Example:
1. Clear the entire activity table using clear t/activity and type the command find t/activity ti/Hans Bo. Since there are no activities yet
(or whenever none of the activities match the queries), the following page will be shown.
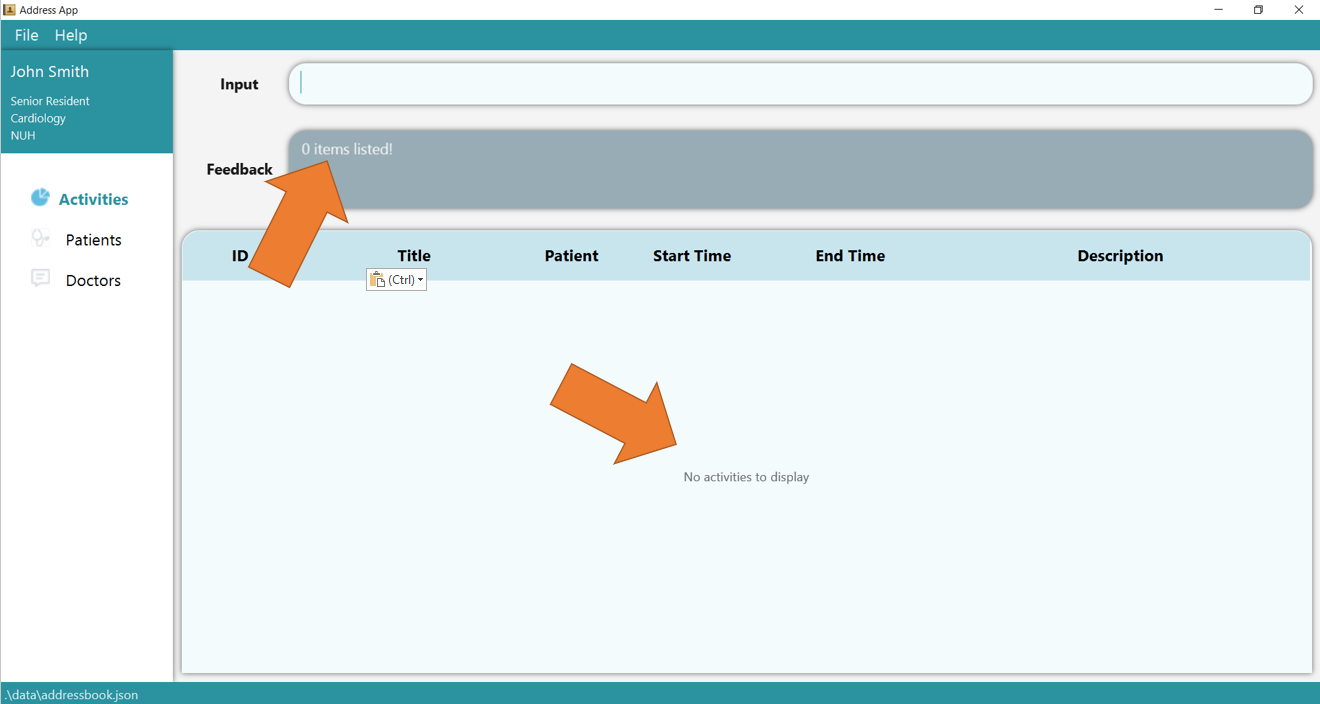
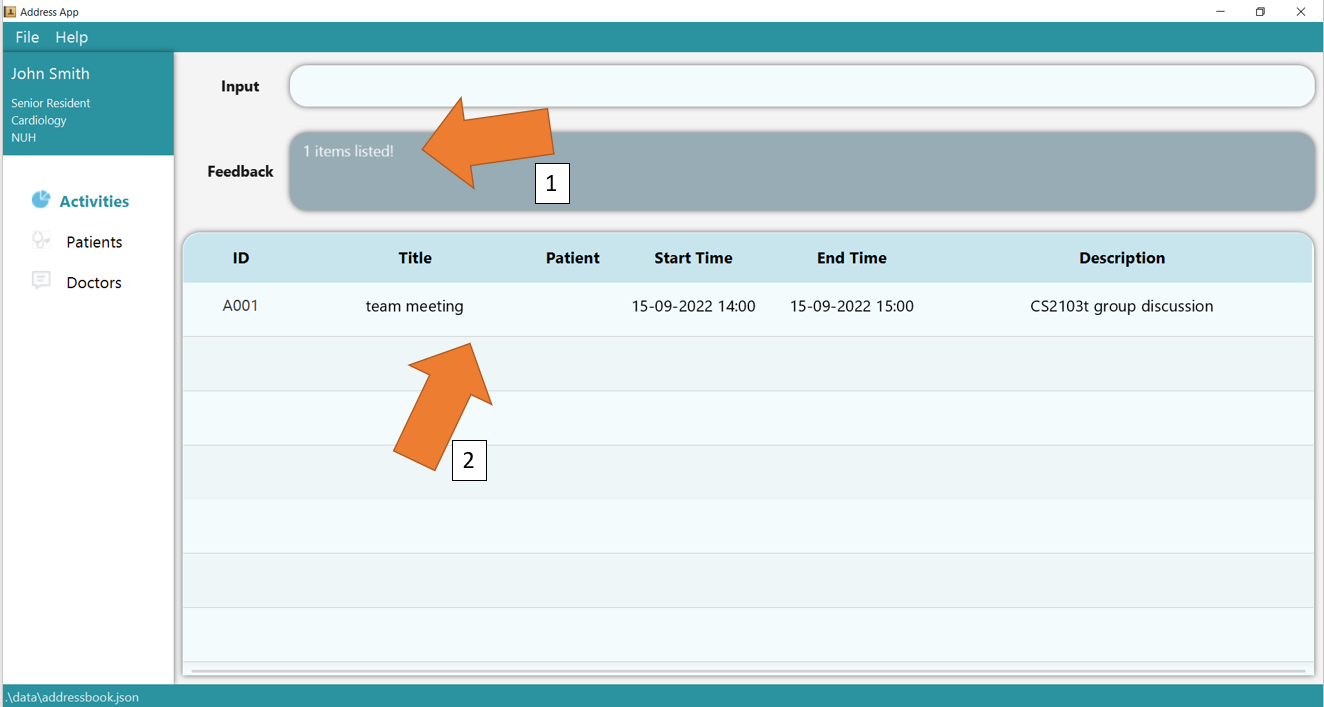
2. Now add 2 new activities using add t/activity s/15/09/2022 14:00 e/15/09/2022 15:00 ti/team meeting d/CS2103t group discussion and
add t/activity s/14/09/2022 11:00 e/14/09/2022 12:00 ti/Lunch with CEO d/Lunch to discuss promotion. To find the activity for team meeting, simply type
find t/activity ti/team meeting. GoMedic would show number of matching records as shown in 1 and display them in the table as shown in 2.
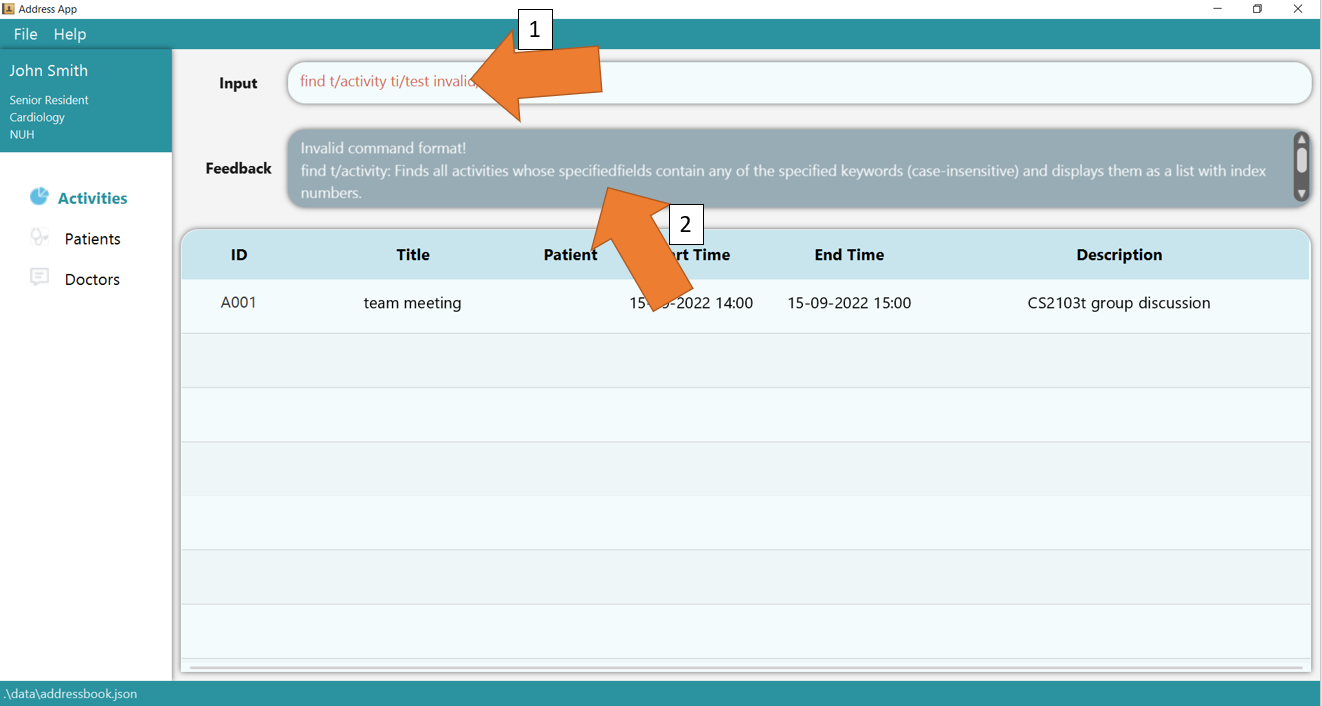
3. If there is any invalid parameters supplied, for e.g. more than 2 fields are supplied, GoMedic will make the commands turn red as shown in 1 and would display the feedback as shown in 2.
To understand better how GoMedic classifies the error messages, please refer to this section.
3.5. General Utility Commands
3.5.1 Generating a referral: referral
Generates a referral letter for a patient in PDF format.
Format: referral ti/TITLE di/DOCTOR_ID pi/PATIENT_ID [d/DESCRIPTION]
The parameters are:
| Parameters | Explanation | Constraints |
|---|---|---|
ti/TITLE |
the title of the referral document. | Must only contain alphanumeric characters and spaces, and it should not be blank |
di/DOCTOR_ID |
id of the doctor to be referred to. | Must be in the form of DXXX / dXXX where XXX is 3-digit integer. For the full information, please refer to this
|
pi/PATIENT_ID |
id of the patient being referred. | Must be in the form of PXXX / pXXX where XXX is 3-digit integer. For full info, please refer to this
|
d/DESCRIPTION |
description of the patient’s condition and further details. | Must only contain alphanumeric characters and spaces, and it should not be blank |
![]() Note:
Note:
- The patient and doctor must both be present in the GoMedic App as a valid entry, else, the referral will not be generated.
- The name of the pdf file will be the title given by the user in the input parameter.
Example:
1. Ensure that Patient P001 and Doctor D001 exist by using list t/patient and list t/doctor accordingly.
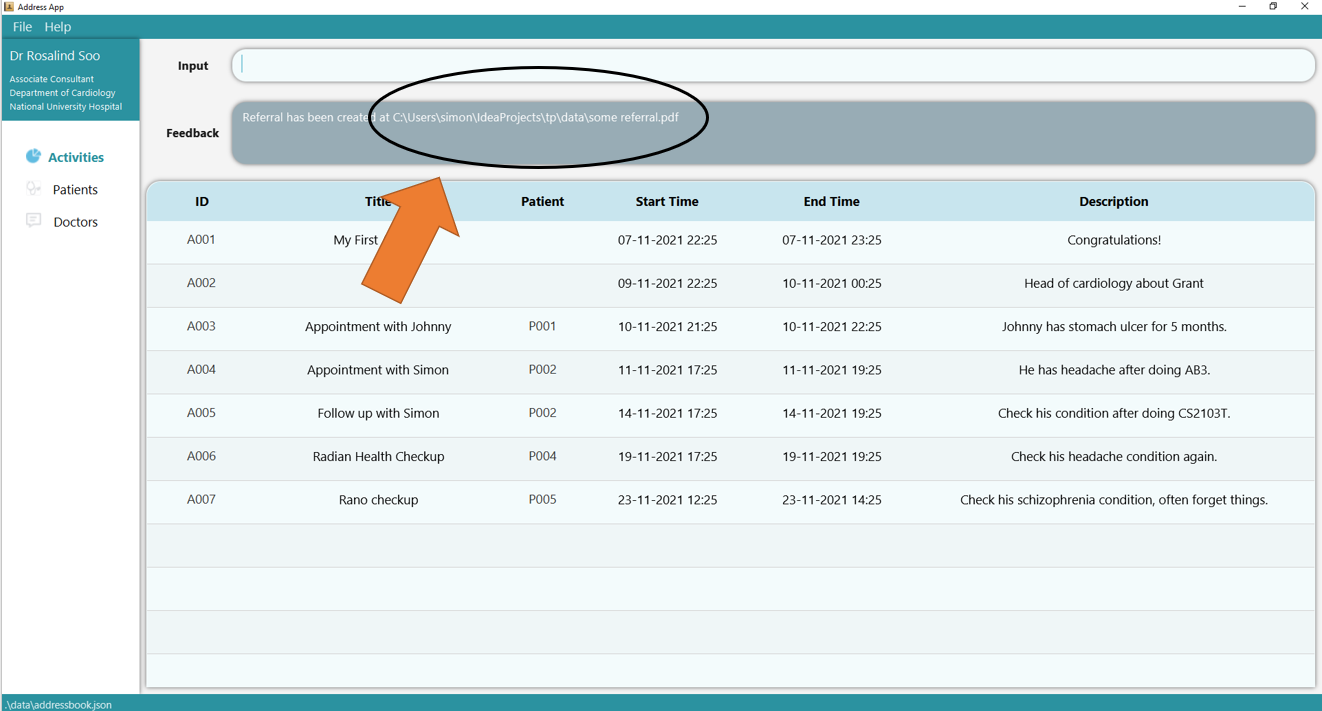
Type the command referral ti/some referral di/D001 pi/P001 into the command box.
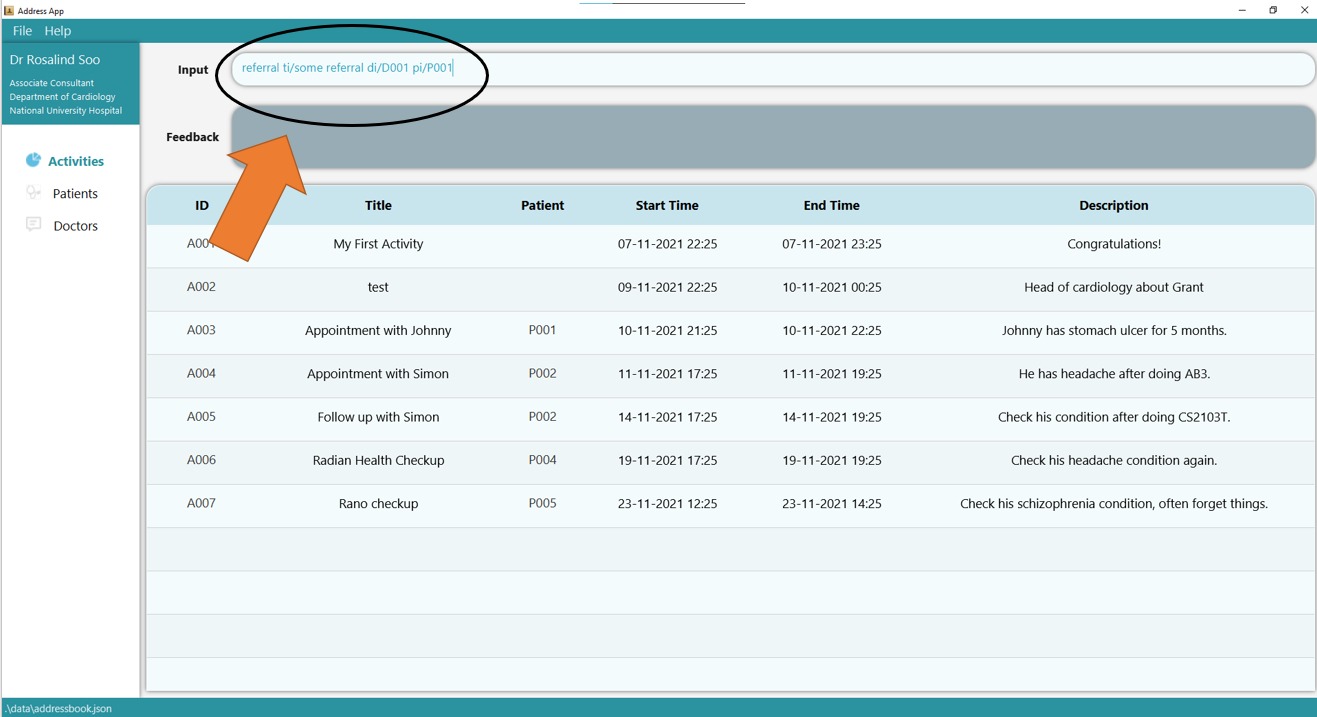
2. Press Enter a referral document will be generated at the specified location in the feedback box.
3.5.2 Customizing your own profile: profile
Updates your profile on GoMedic.
Format: profile n/NAME p/POSITION de/DEPARTMENT o/ORGANIZATION
The parameters are:
| Parameters | Explanation | Constraints |
|---|---|---|
n/NAME |
the name of the doctor. | Must only contain alphanumeric characters and spaces, and it should not be blank |
p/POSITION |
the position held by the doctor. (E.g. Senior consultant) | Must only contain alphanumeric characters and spaces, and it should not be blank |
de/DEPARTMENT |
the department of the doctor. | Must only contain alphanumeric characters and spaces, and it should not be blank |
o/ORGANIZATION |
the organization that the doctor works in. (E.g. National University Hospital) | Must only contain alphanumeric characters and spaces, and it should not be blank |
Example:
1. Type the command profile n/Jon Snow p/Senior Consultant de/Department of Cardiology o/NUH into the command box.
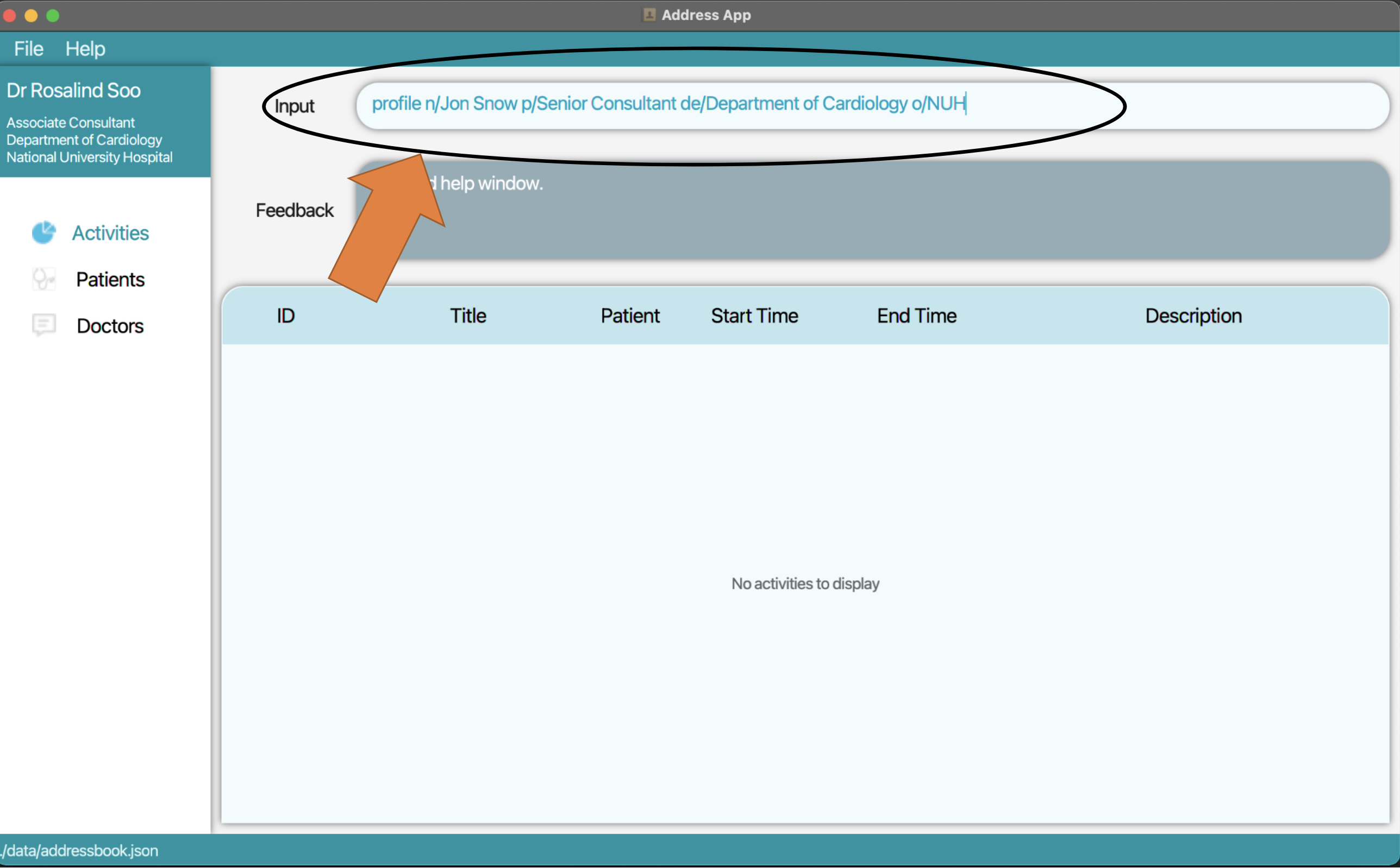
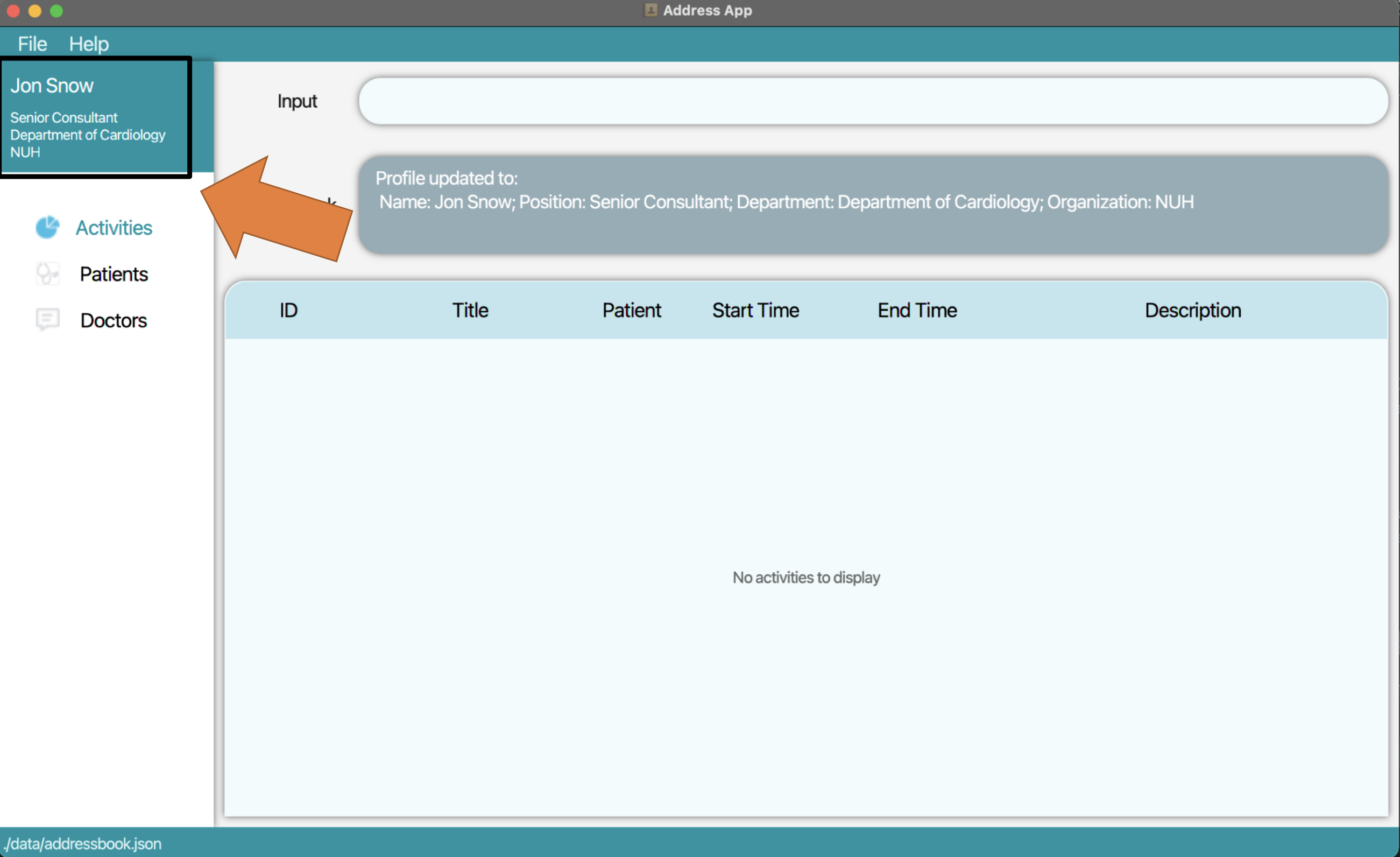
2. Press Enter and your user profile will be updated.
3.5.3 Viewing help : help
Shows a message giving a brief explanation of each command term, with its command format.
Users can also copy a link to this user guide through the help command for more information.
Note:
The in-app window just a basic guideline on how to use commands. Make use of the error messages from invalid commands, or follow the link to the user guide, to get a better understanding of the commands.
Format: help
3.5.4 Clearing all entries : clear
Clears all entries from the address book and resets the user profile to its default.
Format: clear
3.5.5 Exiting the program : exit
Exits the program.
Format: exit
4. Tips and Tricks
4.1 Navigating Past Commands
GoMedic is designed mainly for those who type fast and prefer inputting commands by typing them. However, typing commands repeatedly to fix small errors from previous commands can be frustrating.
![]() Tip: You can navigate to your previous commands by pressing the up or down arrow keys!
Tip: You can navigate to your previous commands by pressing the up or down arrow keys!
Instead of typing the corrected command from scratch, you can press the up or down arrow keys to get the commands that you have entered previously, and modify them accordingly!
- The up arrow key allows you to go back to the previous command typed if any
- The down arrow key allows you to go forward to the next command typed if any
If there are no more commands after the current command in the command box, GoMedic would clear the command box for you!
Examples:
1. Open the app and type list t/patient into the command box. The data shown in your table
might differ from the screenshots, depending on the data that is currently stored in your GoMedic.
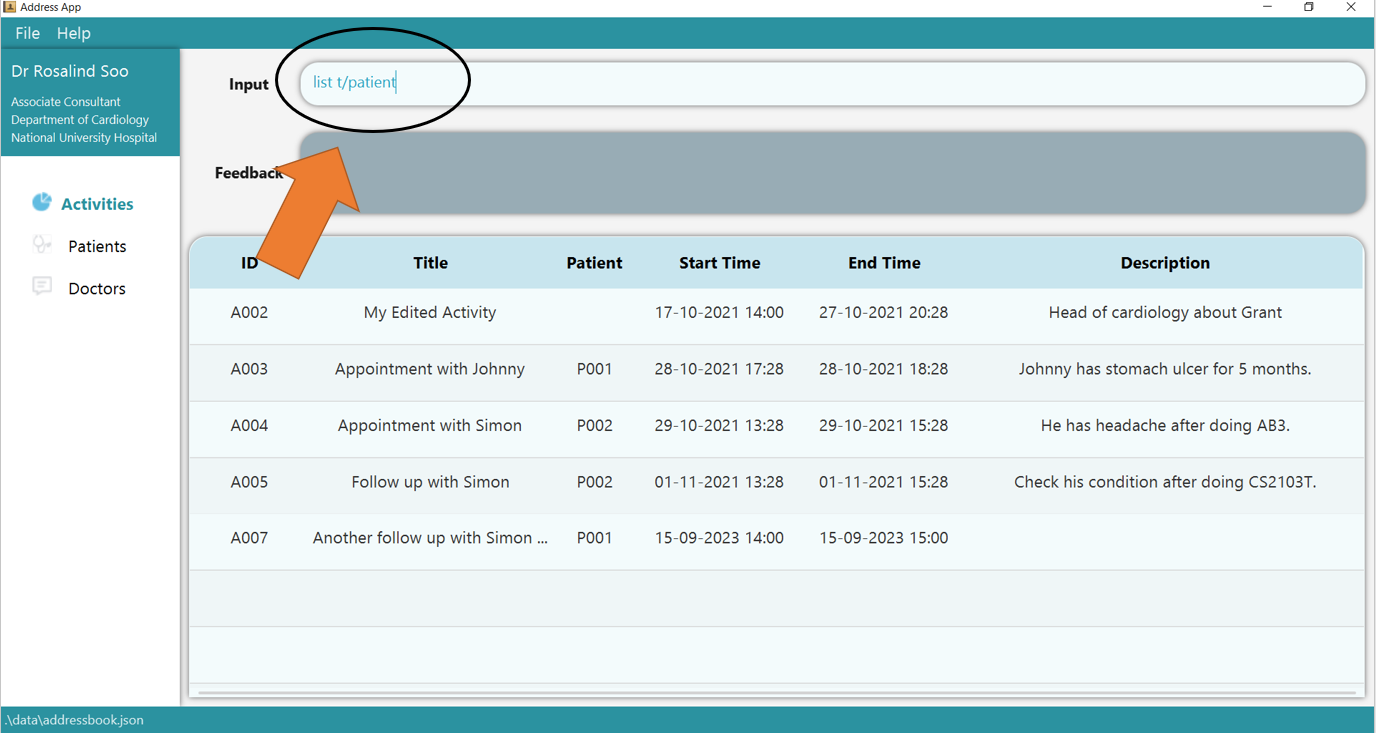
2. Press Enter and you would get the Patient table listed!
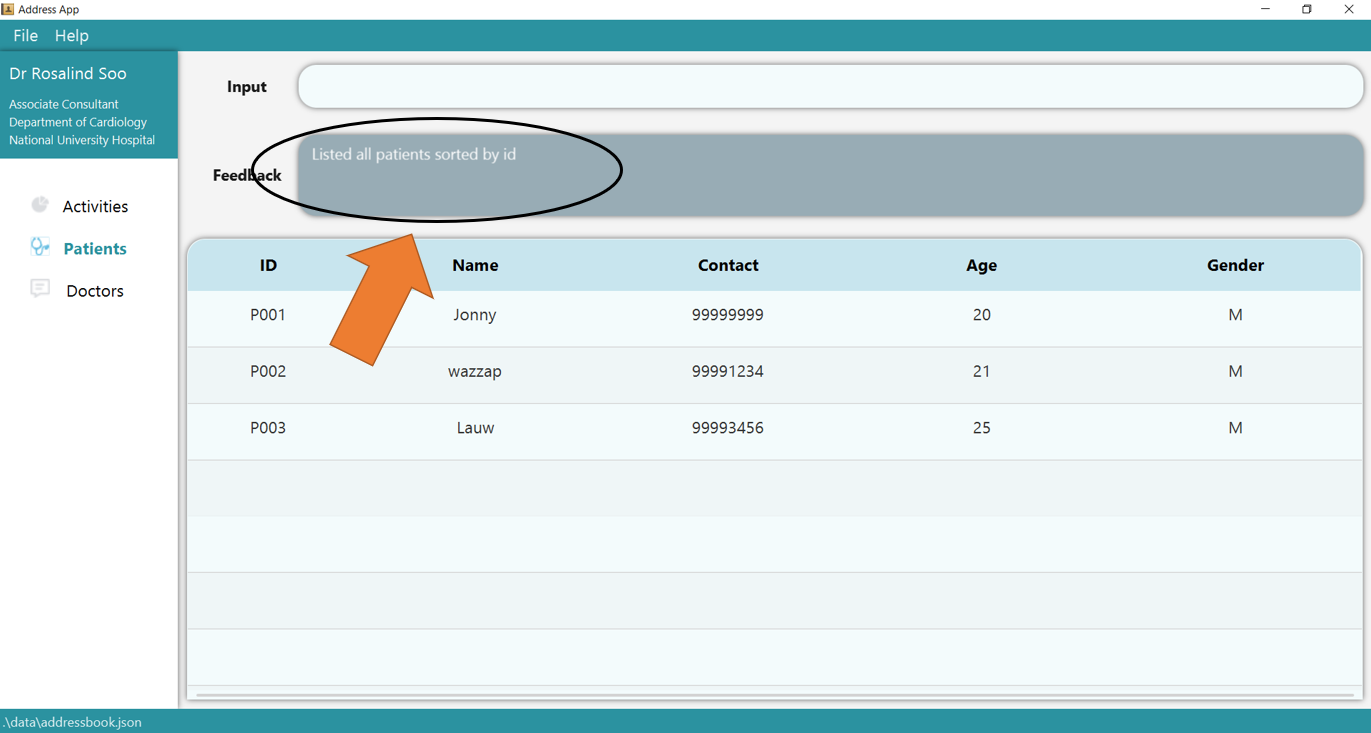
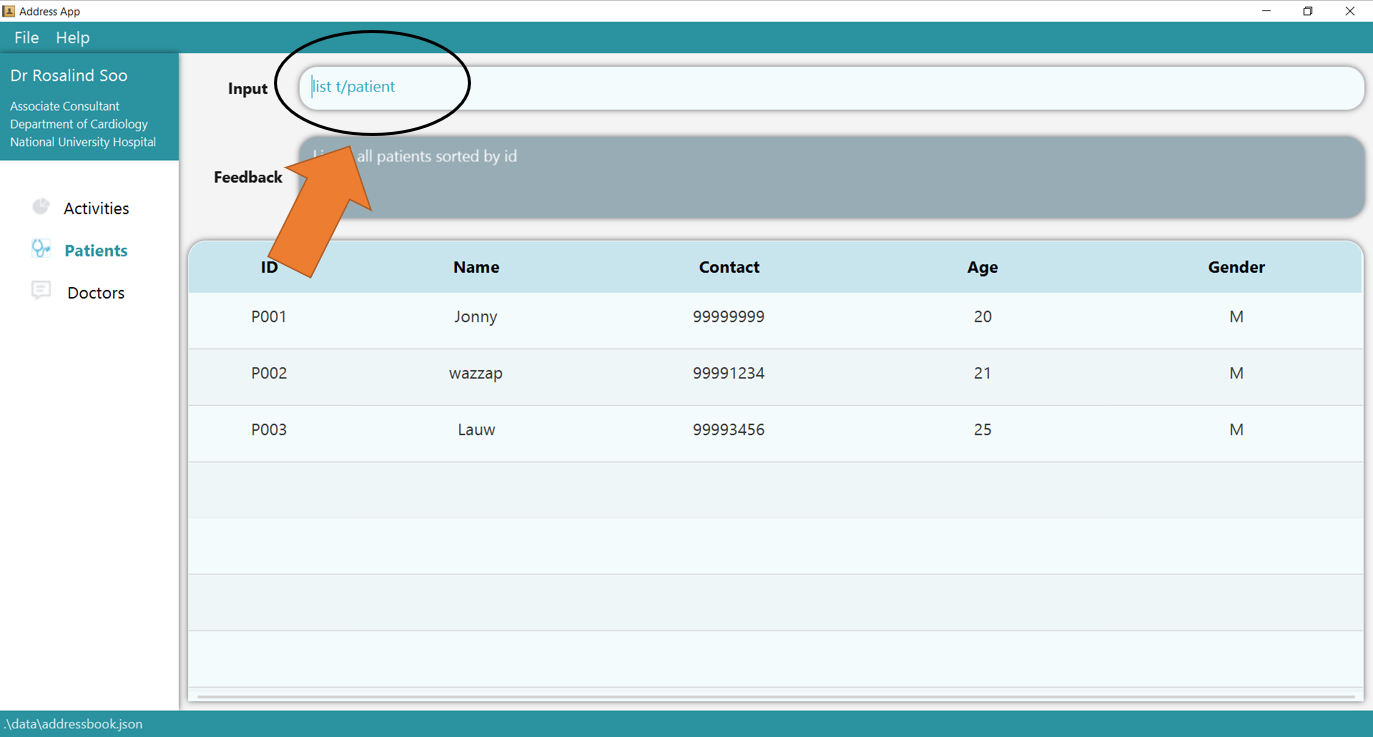
3. To get the list t/patient command again, simply press Up arrow key in your keyboard, and you will get the list t/patient command
in your command box again!
4.2 Suggestions
There are two types of erroneous inputs that we are expecting; One for single worded commands and one for two word commands. Behaviour of each erroneous command is assumed to follow the convention specified above.
- Any mention of
{command}refers to one of these valuesadd,delete,list,edit,clear,find,view,help,profile,referral,help,exit -
{type}indicates one of these three valuest/activity,t/patient,t/doctorand{type}_idmeansACTIVITY_IDfor{type} = t/activity
There will be up to 5 suggested commands for each erroneous input.
-
For errors that follow the format
{misspelt command}-
errors such as
exiwill returnexit,edit t/patient,edit t/doctor,edit t/activityranked using a word similarity metric. -
for such errors, single word commands like
helpor two word commands likeadd t/patientmay be suggested.
-
-
For errors that follow the format
{command} {misspelt type},{misspelt command} {type}or{misspelt command} {misspelt type}:-
errors such as
adl t/patitwill returnadd t/patient,add t/activityranked using a word similarity metric. -
for such errors, only two word commands like
add t/patientcan be suggested.
-
4.3 Saving the data
GoMedic saves the data on the hard disk automatically after every command. There is no need to save manually. Currently, all the data are saved as a JSON file [JAR file location]/data/addressbook.json.
4.4 Editing the data file
GoMedic allows advanced users to update the data stored at [JAR file location]/data/addressbook.json directly by editing that data file.
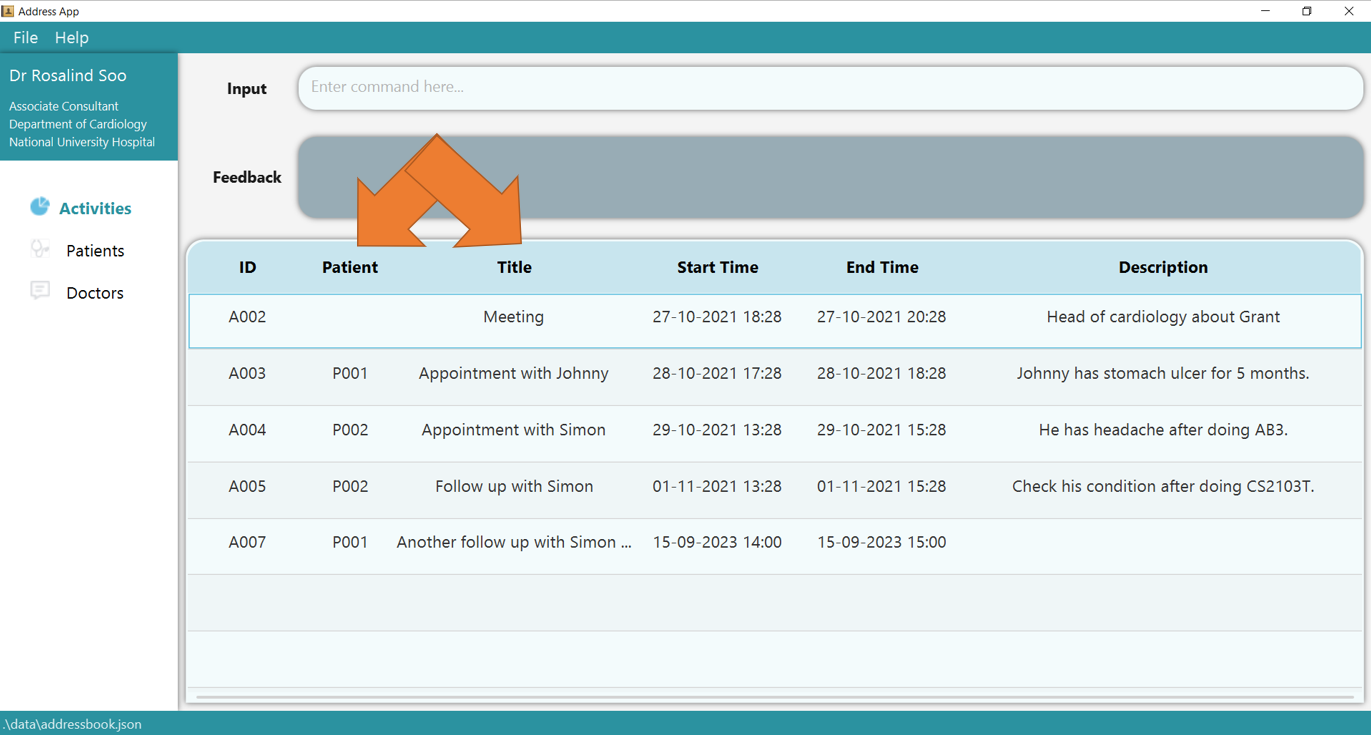
4.5 Reordering Columns in The Display Table
![]() Tip: You can reorder the column to suit your preference by dragging the title, as shown by the following picture.
Tip: You can reorder the column to suit your preference by dragging the title, as shown by the following picture.
1. Left click and hold any header of the table. The column would turn blue, indicating that it can be dragged.
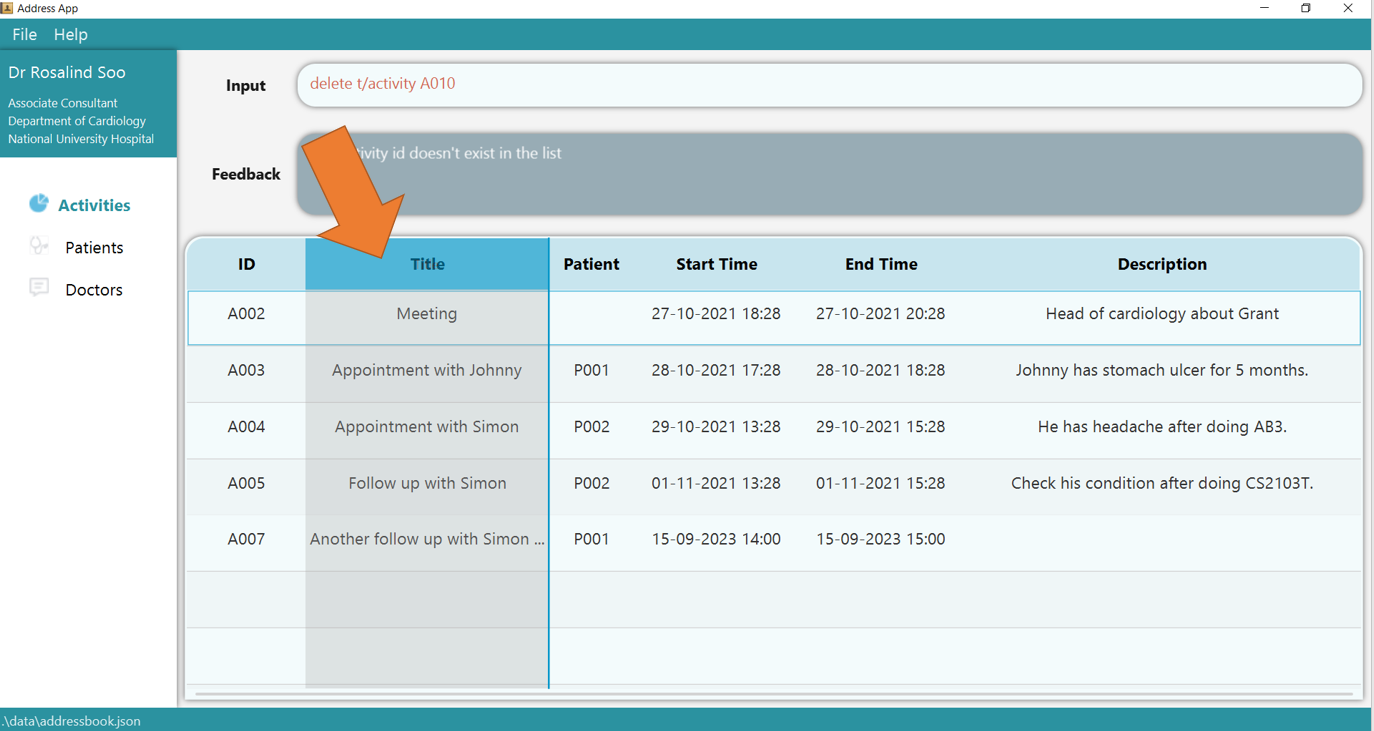
2. Drag the header into the location of other columns as indicated as 1. The column would be inserted at the line indicated by 2.
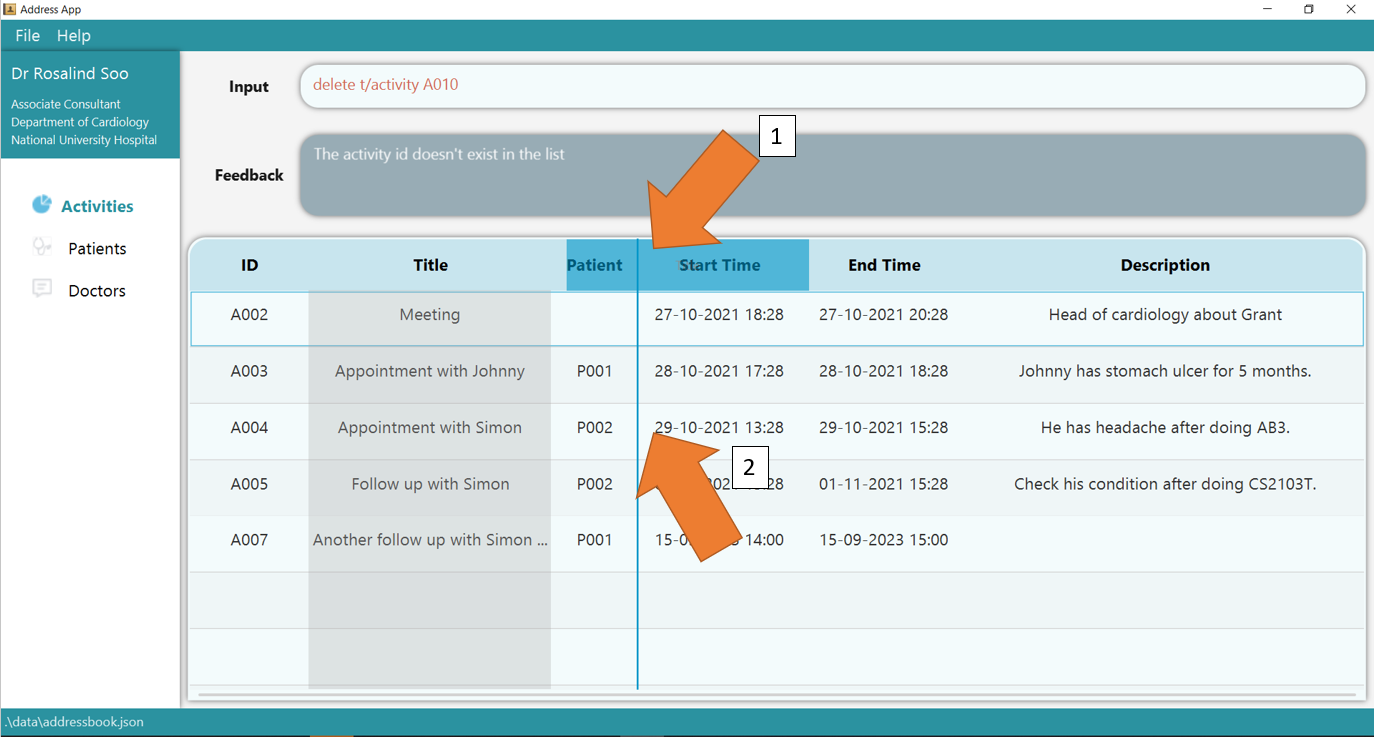
3. Release the left click, and the columns should be reordered now!
5. FAQ
Q: I can’t double-click on the gomedic.jar file to open it. What should I do?
A: Please check that you have Java 11 or above installed in your Computer by opening the terminal. You can do so by entering the command java --version. It should show java 11.x.xx or openjdk 11.x.xx, depending on the Java 11 distribution you are using.
Following that, enter the command java -jar gomedic.jar in the directory that gomedic.jar resides in. Some precautions :
- For Windows user, please do not open it using Windows Subsystem Linux (WSL), please use Windows PowerShell to run
gomedic.jar - For Mac users, you can follow the precautions stated here to open your
jarfile. - If the aforementioned steps do not help you, please contact our developers directly by raising a new issue here!
Q: What are config.json, preferences.json and addressbook.log stored in [JAR file location]/data/addressbook.json ?
A: config.json and preferences.json are programmable files that contains default settings that GoMedic uses such as the height and the width of the application, location to save the data, etc. Advanced users are welcome to edit it but
please take note of these precautions!
Meanwhile, addressbook.log is a text file containing messages for developers to fix some errors that the Users face. Should you want to raise a new issue about a new bug, you can always attach
all the log files too so that we can help you find the root cause of the error faster!
Q: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
A: Install the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data folder that it creates with the old data folder created by the old GoMedic application together with all the files within that data folder!
6. Command summary
-
{PARAMETERS}indicates the mandatory and optional parameters as specified in the Features section. -
{type}indicates one of these three valuest/activity,t/patient,t/doctorand{type}_idmeansACTIVITY_IDfor{type} = t/activity
| Action | Format | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Add | add {type} {PARAMETERS} |
add t/doctor n/Timmy Tom p/98765432 de/neurology |
| Delete | delete {type} {type}_ID |
delete t/patient P003 |
| Edit | edit {type} i/{type}_ID ... |
edit t/patient i/P123 n/John Doe a/30 g/M |
| Find | find {type} ... |
find ta/important ti/tutorial |
| View | view t/patient PATIENT_ID |
view t/patient P003 |
| Referral | referral {PARAMETERS} |
referral ti/Referral of Patient A di/D001 pi/P001 |
| Profile | profile {PARAMETERS} |
profile n/Jon Snow p/Senior Consultant de/Department of Cardiology o/NUH |
| Clear |
clear or clear {type}
|
clear t/activity |
| List | list {type} {PARAMETERS} |
list t/patient, list t/activity s/START
|
| Exit | exit |
|
| Help | help |
For additional tips and tricks such as past commands navigation and table columns reordering, please refer to this section!